Detection of Poly- and Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) in U.S. Drinking Water Linked to Industrial Sites, Military Fire Training Areas, and Wastewater Treatment Plants
- PMID: 27752509
- PMCID: PMC5062567
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.estlett.6b00260
Detection of Poly- and Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) in U.S. Drinking Water Linked to Industrial Sites, Military Fire Training Areas, and Wastewater Treatment Plants
Abstract
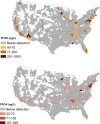
Drinking water contamination with poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) poses risks to the developmental, immune, metabolic, and endocrine health of consumers. We present a spatial analysis of 2013-2015 national drinking water PFAS concentrations from the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency's (US EPA) third Unregulated Contaminant Monitoring Rule (UCMR3) program. The number of industrial sites that manufacture or use these compounds, the number of military fire training areas, and the number of wastewater treatment plants are all significant predictors of PFAS detection frequencies and concentrations in public water supplies. Among samples with detectable PFAS levels, each additional military site within a watershed's eight-digit hydrologic unit is associated with a 20% increase in PFHxS, a 10% increase in both PFHpA and PFOA, and a 35% increase in PFOS. The number of civilian airports with personnel trained in the use of aqueous film-forming foams is significantly associated with the detection of PFASs above the minimal reporting level. We find drinking water supplies for 6 million U.S. residents exceed US EPA's lifetime health advisory (70 ng/L) for PFOS and PFOA. Lower analytical reporting limits and additional sampling of smaller utilities serving <10000 individuals and private wells would greatly assist in further identifying PFAS contamination sources.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kissa E.Fluorinated surfactants and repellents, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, 2001.
-
- Lewis R. C.; Johns L. E.; Meeker J. D. Serum Biomarkers of Exposure to Perfluoroalkyl Substances in Relation to Serum Testosterone and Measures of Thyroid Function among Adults and Adolescents from NHANES 2011–2012. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12 (6), 6098–6114. 10.3390/ijerph120606098. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fourth National Report on Human Exposure to Environmental Chemicals; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Atlanta, 2015.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous