Preventable trauma death rate in Daegu, South Korea
- PMID: 27752603
- PMCID: PMC5052913
- DOI: 10.15441/ceem.15.085
Preventable trauma death rate in Daegu, South Korea
Abstract
Objective: This study investigated the preventable death rate in Daegu, South Korea, and assessed affecting factors and preventable factors in order to improve the treatment of regional trauma patients.
Methods: All traumatic deaths between January 2012 and December 2012 in 5 hospitals in Daegu were analyzed by panel review, which were classified into preventable and non-preventable deaths. We determined the factors affecting trauma deaths and the preventable factors during trauma care.
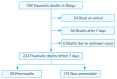
Results: There were overall 358 traumatic deaths during the study period. Two hundred thirty four patients were selected for the final analysis after excluding cases of death on arrival, delayed death, and unknown causes. The number of preventable death was 59 (25.2%), which was significantly associated with mode of arrival, presence of head injury, date, and time of injury. A multivariate analysis revealed that preventable death was more likely when patients were secondly transferred from another hospital, visited hospital during non-office hour, and did not have head injuries. The panel discovered 145 preventable factors, which showed that majority of factors occurred in emergency departments (49.0%), and were related with system process (76.6%).
Conclusion: The preventable trauma death rate in Daegu was high, and mostly process-related.
Keywords: Death; Outcome and process assessment; Secondary prevention; Wounds and injuries.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
Similar articles
-
National Follow-up Survey of Preventable Trauma Death Rate in Korea.J Korean Med Sci. 2022 Dec 26;37(50):e349. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2022.37.e349. J Korean Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 36573386 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic Preventable Trauma Death Rate Survey to Establish the Region-based Inclusive Trauma System in a Representative Province of Korea.J Korean Med Sci. 2020 Dec 28;35(50):e417. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e417. J Korean Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 33372420 Free PMC article.
-
Preventable trauma deaths in Singapore.Aust N Z J Surg. 1998 Dec;68(12):820-5. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1622.1998.01461.x. Aust N Z J Surg. 1998. PMID: 9885861
-
Comparison of Preventable Trauma Death Rates in Patients With Traumatic Brain Injury Before and After the Establishment of Regional Trauma Center: A Single Center Experience.Korean J Neurotrauma. 2023 May 26;19(2):227-233. doi: 10.13004/kjnt.2023.19.e16. eCollection 2023 Jun. Korean J Neurotrauma. 2023. PMID: 37431367 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ranking Hospitals Based on Preventable Hospital Death Rates: A Systematic Review With Implications for Both Direct Measurement and Indirect Measurement Through Standardized Mortality Rates.Milbank Q. 2019 Mar;97(1):228-284. doi: 10.1111/1468-0009.12375. Milbank Q. 2019. PMID: 30883952 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Relationships between trauma death, disability, and geographic factors: a systematic review.Clin Exp Emerg Med. 2023 Dec;10(4):426-437. doi: 10.15441/ceem.23.009. Epub 2023 Aug 1. Clin Exp Emerg Med. 2023. PMID: 37525580 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Trauma Center Establishment on the Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes of Patients with Traumatic Brain Injury : A Retrospective Analysis from a Single Trauma Center in Korea.J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2019 Mar;62(2):232-242. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2018.0037. Epub 2019 Feb 27. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2019. PMID: 30840979 Free PMC article.
-
A Propensity Score-Matched Comparison of In-Hospital Mortality between Dedicated Regional Trauma Centers and Emergency Medical Centers in the Republic of Korea.Emerg Med Int. 2022 Nov 16;2022:5749993. doi: 10.1155/2022/5749993. eCollection 2022. Emerg Med Int. 2022. PMID: 36438862 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of polymorphonuclear cell apoptosis and inflammatory cytokines in trauma patients in the emergency department.Am J Transl Res. 2021 Sep 15;13(9):10617-10624. eCollection 2021. Am J Transl Res. 2021. PMID: 34650734 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Surgical Mortalities Using the Fishbone Model for Quality Improvement in Surgical Disciplines.World J Surg. 2022 May;46(5):1006-1014. doi: 10.1007/s00268-021-06414-8. Epub 2022 Feb 4. World J Surg. 2022. PMID: 35119512
References
-
- Korean Statistical Information Service . Daejeon: Statistics Korea; 2014. Deaths, death rates, age-standardized death rates by cause (50 item) and sex: si, gun, and gu [Internet] [cited 2015 Aug 31]. Available from: http://kosi.kr/statisticsList/statisticsList_01List.jsp?vwcd=MT_ZTITLE&p....
-
- Rutstein DD, Berenberg W, Chalmers TC, Child CG, 3rd, Fishman AP, Perrin EB. Measuring the quality of medical care: a clinical method. N Engl J Med. 1976;294:582–8. - PubMed
-
- Settervall CH, Domingues Cde A, Sousa RM, Nogueira Lde S. Preventable trauma deaths. Rev Saude Publica. 2012;46:367–75. - PubMed
-
- Jung KY, Kim JS, Kim Y. Problems in trauma care and preventable deaths. J Korean Soc Emerg Med. 2001;12:45–56.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical