Detection of vertebral metastases: a meta-analysis comparing MRI, CT, PET, BS and BS with SPECT
- PMID: 27752772
- PMCID: PMC11819241
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-016-2288-z
Detection of vertebral metastases: a meta-analysis comparing MRI, CT, PET, BS and BS with SPECT
Abstract
Objective: To perform a meta-analysis to compare the diagnostic value of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), computed tomography (CT), positron emission tomography (PET), bone scintigraphy (BS) and BS with single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) in detecting vertebral metastases.
Methods: Relevant original articles published from January 1995 to December 2015 were searched. Two reviewers independently extracted data. Software called "META-DiSc" was used to obtain pooled estimates of sensitivity, specificity, diagnostic odds ratio (DOR) and summary receiver operating characteristic (SROC) curves.
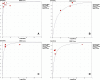
Results: Twenty-three articles consisting of 33 studies fulfilled all inclusion criteria. On per-patient basis, for sensitivity, MRI = PET = SPECT > CT = BS ("=" indicated no significant difference, P > 0.05; ">" indicated significantly higher, P < 0.05). For specificity, MRI = CT = BS > SPECT > PET. For DOR, MRI > SPECT > BS > CT = PET. SROC curves for SPECT and MRI showed better diagnostic accuracy than others. On per-lesion basis, for sensitivity, PET = SPECT = MRI > BS > CT. For specificity, MRI = CT > PET = SPECT = BS. For DOR, MRI > SPECT > CT = PET > BS. SROC curves showed MRI had the best while CT had the lowest diagnostic accuracy.
Conclusion: For diagnosis of vertebral metastases, MRI was found to be the best modality and also better than other techniques on both per-patient and per-lesion basis.
Keywords: BS; MRI; Meta-analysis; PET; Vertebral metastases.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A meta-analysis of 18FDG-PET, MRI and bone scintigraphy for diagnosis of bone metastases in patients with breast cancer.Skeletal Radiol. 2011 May;40(5):523-31. doi: 10.1007/s00256-010-0963-8. Epub 2010 May 22. Skeletal Radiol. 2011. PMID: 20495798
-
FDG-PET, CT, MRI for diagnosis of local residual or recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma, which one is the best? A systematic review.Radiother Oncol. 2007 Dec;85(3):327-35. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2007.11.002. Epub 2007 Nov 26. Radiother Oncol. 2007. PMID: 18037523
-
123I-MIBG scintigraphy and 18F-FDG-PET imaging for diagnosing neuroblastoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Sep 29;2015(9):CD009263. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009263.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 26417712 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of 18F-FDG PET/CT, MRI and SPECT in the diagnosis of local residual/recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A meta-analysis.Oral Oncol. 2016 Jan;52:11-7. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2015.10.010. Epub 2015 Nov 4. Oral Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26547126
-
Computed tomography versus magnetic resonance imaging versus bone scintigraphy for clinically suspected scaphoid fractures in patients with negative plain radiographs.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Jun 5;2015(6):CD010023. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010023.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 26045406 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC): A potential in vivo biological surrogate of the incidentally discovered bone lesions at 3T MRI.Eur J Radiol Open. 2021 Nov 25;8:100386. doi: 10.1016/j.ejro.2021.100386. eCollection 2021. Eur J Radiol Open. 2021. PMID: 34877369 Free PMC article.
-
Ten Years After SINS: Role of Surgery and Radiotherapy in the Management of Patients With Vertebral Metastases.Front Oncol. 2022 Jan 27;12:802595. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.802595. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35155240 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Progress in Technetium-99m-Labeled Nanoparticles for Molecular Imaging and Cancer Therapy.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021 Nov 10;11(11):3022. doi: 10.3390/nano11113022. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34835786 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diagnostic accuracy of imaging modalities for detection of spinal metastases: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Clin Transl Oncol. 2025 May;27(5):2316-2326. doi: 10.1007/s12094-024-03765-1. Epub 2024 Oct 29. Clin Transl Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39470945 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of metastatic lesion on the structural determinants of bone: Current clinical and experimental approaches.Bone. 2020 Sep;138:115159. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2019.115159. Epub 2019 Nov 21. Bone. 2020. PMID: 31759204 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Algra PR, Heimans JJ, Valk J, Nauta J, Lachniet M, Van Kooten B (1992) Do metastases in vertebrae begin in the body or the pedicles? Imaging study in 45 patients. Am J Roentgenol 158:1275–1279 - PubMed
-
- Asdourian PL, Weidenbaum M, DeWald RL, Hammerberg KW, Ramsey RG (1990) The pattern of vertebral involvement in metastatic vertebral breast cancer. Clin Orthop Relat Res 250:164–170 - PubMed
-
- Berlin JA (1997) Does blinding of readers affect the results of meta-analyses? The Lancet 350:185–186 - PubMed
-
- Bilsky MH, Lis E, Raizer J, Lee H, Boland P (1999) The diagnosis and treatment of metastatic spinal tumor. Oncologist 4:459–469 - PubMed
-
- Blake GM, Park-Holohan S-J, Cook GJ, Fogelman I (2001) Quantitative studies of bone with the use of 18 F-fluoride and 99 m Tc-methylene diphosphonate Seminars in nuclear medicine. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 28–49 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

