Metronomic chemotherapy with oral vinorelbine (mVNR) and capecitabine (mCAPE) in advanced HER2-negative breast cancer patients: is it a way to optimize disease control? Final results of the VICTOR-2 study
- PMID: 27752847
- PMCID: PMC5090011
- DOI: 10.1007/s10549-016-4009-3
Metronomic chemotherapy with oral vinorelbine (mVNR) and capecitabine (mCAPE) in advanced HER2-negative breast cancer patients: is it a way to optimize disease control? Final results of the VICTOR-2 study
Abstract
Purpose: The VICTOR-1 study demonstrated that the all-oral metronomic combination of vinorelbine and capecitabine is highly active and well tolerated in hormone receptor-positive/HER2-negative patients. The VICTOR-2 study was designed to confirm these results.
Methods: Patients received mVNR 40 mg three times a week and mCAPE 500 mg three times a day, continuously. The primary endpoint was the clinical benefit rate (CBR); secondary endpoints were toxicity, objective response rate (ORR), and progression-free survival (PFS).
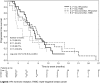
Results: Eighty patients were evaluable for the primary efficacy analysis. Median age was 65.3 years; most patients had HR-positive tumors (65 %). The CBR was 45.7 % (95 % CI 28.8-63.4) and 51.1 % (95 % CI 35.8-66.3) in first- and ≥ second-line therapy, respectively. The ORR was 35.5 % in first-line (95 % CI 19.2-54.6) and 25.6 % in ≥second-line (95 % CI 13.5-41.2). The median duration of response was 11.3 and 6.4 months and PFS rates at 1 year were 24.3 and 22.2 %, respectively. In triple-negative breast cancer patients (N = 28, 35 %) a lower, but clinically relevant CBR (35.7, 95 % CI 18.6-55.9) was observed. The main toxicities per cycle were non-febrile neutropenia (1.1 %), hand-foot syndrome (1.0 %), nausea and vomiting (1.0 %), leucopenia (0.8 %), fatigue (0.7 %), and diarrhea (0.4 %).
Conclusion: The VICTOR-2 study confirms the clinical activity of mVNR and mCAPE in HER2-negative breast cancer patients, suggesting that the easy schedule of administration, which requires monthly blood tests and limits patients' dependence on hospitals, and the low cost of the drugs are valuable elements, even for countries with limited access to innovative or expensive drugs.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Capecitabine; Metronomic chemotherapy; Vinorelbine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared no conflicts of interest. Informed consent The study was conducted in accordance with the 1987 Declaration of Helsinki and adhered to Good Clinical Practice guidelines. Approval of the protocol was obtained from the local ethics committee for each participating center; all patients were required to give written informed consent before enrolment and to comply with the protocol for the duration of the study.
Figures
Comment in
-
First-line all-oral NORCAP (vinorelbine/capecitabine) might be alternative to taxane-based chemotherapy for HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2017 Jan;161(2):385. doi: 10.1007/s10549-016-4055-x. Epub 2016 Nov 17. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2017. PMID: 27858315 No abstract available.
-
In reply to Kadri Altundag.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2017 Jan;161(2):387. doi: 10.1007/s10549-016-4056-9. Epub 2016 Nov 21. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2017. PMID: 27873134 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Oral vinorelbine in combination with trastuzumab as a first-line therapy of metastatic or locally advanced HER2-positive breast cancer.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2016 May;77(5):1069-77. doi: 10.1007/s00280-016-3027-5. Epub 2016 Apr 8. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27059339 Clinical Trial.
-
SAKK 24/09: safety and tolerability of bevacizumab plus paclitaxel vs. bevacizumab plus metronomic cyclophosphamide and capecitabine as first-line therapy in patients with HER2-negative advanced stage breast cancer - a multicenter, randomized phase III trial.BMC Cancer. 2016 Oct 10;16(1):780. doi: 10.1186/s12885-016-2823-y. BMC Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27724870 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Safety and efficacy of vinorelbine in combination with pertuzumab and trastuzumab for first-line treatment of patients with HER2-positive locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer: VELVET Cohort 1 final results.Breast Cancer Res. 2016 Dec 13;18(1):126. doi: 10.1186/s13058-016-0773-6. Breast Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27955684 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
[Oral vinorelbine: pharmacology and treatment outcome in non-small cell bronchial carcinoma and breast carcinoma].Onkologie. 2006 Mar;29 Suppl 1:1-28. doi: 10.1159/000091889. Epub 2006 Mar 3. Onkologie. 2006. PMID: 16534241 Review. German.
-
Metronomic chemotherapy combined with endocrine therapy: are we challenging some dogmas?Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2020 Jul;20(7):563-573. doi: 10.1080/14737140.2020.1782200. Epub 2020 Jun 30. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2020. PMID: 32536212 Review.
Cited by
-
Co-targeting triple-negative breast cancer cells and endothelial cells by metronomic chemotherapy inhibits cell regrowth and migration via downregulation of the FAK/VEGFR2/VEGF axis and autophagy/apoptosis activation.Front Oncol. 2022 Nov 30;12:998274. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.998274. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36531071 Free PMC article.
-
Real-world data on the efficacy and safety of weekly oral vinorelbine in breast cancer patients previously treated with anthracycline or taxane-based regimens.Clin Transl Oncol. 2019 Apr;21(4):459-466. doi: 10.1007/s12094-018-1946-9. Epub 2018 Oct 6. Clin Transl Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30293232
-
Metronomic chemotherapy (mCHT) in metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) patients: results of the VICTOR-6 study.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2021 Dec;190(3):415-424. doi: 10.1007/s10549-021-06375-5. Epub 2021 Sep 21. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2021. PMID: 34546500 Free PMC article.
-
Metronomic Chemotherapy.Cancers (Basel). 2021 May 6;13(9):2236. doi: 10.3390/cancers13092236. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34066606 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metronomic Chemotherapy in Triple-Negative Metastatic Breast Cancer: The Future Is Now?Int J Breast Cancer. 2017;2017:1683060. doi: 10.1155/2017/1683060. Epub 2017 Dec 3. Int J Breast Cancer. 2017. PMID: 29333297 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cazzaniga ME, Torri V, Villa F, et al. Efficacy and safety of the all-oral schedule of metronomic vinorelbine and capecitabine in locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer patients: the phase I-II VICTOR-1 study. Int J Breast Cancer. 2014;2014:769790. doi: 10.1155/2014/769790. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Montagna E, Lai A, Palazzo A, et al. A phase II study of metronomic oral chemotherapy for metastatic breast cancer patients: Safety and efficacy results of vinorelbine, cyclophosphamide plus capecitabine (VEX) combination. Eur J Cancer Congr. 2015;51:S291–S292. doi: 10.1016/S0959-8049(16)30826-7. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous