Novel functions for the transcription factor E2F4 in development and disease
- PMID: 27753528
- PMCID: PMC5176148
- DOI: 10.1080/15384101.2016.1234551
Novel functions for the transcription factor E2F4 in development and disease
Abstract
The E2F family of transcription factors is a key determinant of cell proliferation in response to extra- and intra-cellular signals. Within this family, E2F4 is a transcriptional repressor whose activity is critical to engage and maintain cell cycle arrest in G0/G1 in conjunction with members of the retinoblastoma (RB) family. However, recent observations challenge this paradigm and indicate that E2F4 has a multitude of functions in cells besides this cell cycle regulatory role, including in embryonic and adult stem cells, during regenerative processes, and in cancer. Some of these new functions are independent of the RB family and involve direct activation of target genes. Here we review the canonical functions of E2F4 and discuss recent evidence expanding the role of this transcription factor, with a focus on cell fate decisions in tissue homeostasis and regeneration.
Keywords: E2F; E2F4; RB; cancer; cell cycle; development; differentiation; regeneration; stem cells.
Figures
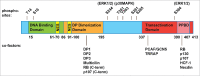
Similar articles
-
E2F4 regulates transcriptional activation in mouse embryonic stem cells independently of the RB family.Nat Commun. 2019 Jul 3;10(1):2939. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-10901-x. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31270324 Free PMC article.
-
E2F4-RB and E2F4-p107 complexes suppress gene expression by transforming growth factor beta through E2F binding sites.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 May 13;94(10):4948-53. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.10.4948. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997. PMID: 9144170 Free PMC article.
-
E2F4 cooperates with pRB in the development of extra-embryonic tissues.Dev Biol. 2009 Aug 1;332(1):104-15. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2009.05.541. Epub 2009 May 9. Dev Biol. 2009. PMID: 19433082 Free PMC article.
-
E2F4 function in G2: maintaining G2-arrest to prevent mitotic entry with damaged DNA.Cell Cycle. 2007 May 15;6(10):1147-52. doi: 10.4161/cc.6.10.4259. Epub 2007 May 11. Cell Cycle. 2007. PMID: 17507799 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interplay between NRF1, E2F4 and MYC transcription factors regulating common target genes contributes to cancer development and progression.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2018 Oct;41(5):465-484. doi: 10.1007/s13402-018-0395-3. Epub 2018 Jul 25. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2018. PMID: 30047092 Review.
Cited by
-
Long noncoding RNA expression analysis reveals the regulatory effects of nitinol-based nanotubular coatings on human coronary artery endothelial cells.Int J Nanomedicine. 2019 May 7;14:3297-3309. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S204067. eCollection 2019. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019. PMID: 31190794 Free PMC article.
-
An Overfeeding-Induced Obesity Mouse Model Reveals Necessity for Sin3a in Postnatal Peak β-Cell Mass Acquisition.Diabetes. 2022 Nov 1;71(11):2395-2401. doi: 10.2337/db22-0306. Diabetes. 2022. PMID: 35944274 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated multi-omics analysis of RB-loss identifies widespread cellular programming and synthetic weaknesses.Commun Biol. 2021 Aug 17;4(1):977. doi: 10.1038/s42003-021-02495-2. Commun Biol. 2021. PMID: 34404904 Free PMC article.
-
A Mutant Variant of E2F4 Triggers Multifactorial Therapeutic Effects in 5xFAD Mice.Mol Neurobiol. 2022 May;59(5):3016-3039. doi: 10.1007/s12035-022-02764-z. Epub 2022 Mar 7. Mol Neurobiol. 2022. PMID: 35254651 Free PMC article.
-
E2F4-Based Gene Therapy Mitigates the Phenotype of the Alzheimer's Disease Mouse Model 5xFAD.Neurotherapeutics. 2021 Oct;18(4):2484-2503. doi: 10.1007/s13311-021-01151-1. Epub 2021 Nov 11. Neurotherapeutics. 2021. PMID: 34766258 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chinnam M, Goodrich DW. RB1, development, and cancer. Curr Top Dev Biol 2011; 94:129-69; PMID:21295686; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-380916-2.00005-X - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Conklin JF, Baker J, Sage J. The RB family is required for the self-renewal and survival of human embryonic stem cells. Nat Commun 2012; 3:1244; PMID:23212373; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/ncomms2254 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dyson NJ. RB1: a prototype tumor suppressor and an enigma. Genes Dev 2016; 30:1492-502; PMID:27401552; http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/gad.282145.116 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dimova DK, Dyson NJ. The E2F transcriptional network: old acquaintances with new faces. Oncogene 2005; 24:2810-26; PMID:15838517; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208612 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lammens T, Li J, Leone G, De Veylder L. Atypical E2Fs: new players in the E2F transcription factor family. Trends Cell Biol 2009; 19:111-8; PMID:19201609; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.tcb.2009.01.002 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
