Estrogen induces RAD51C expression and localization to sites of DNA damage
- PMID: 27753535
- PMCID: PMC5176134
- DOI: 10.1080/15384101.2016.1241927
Estrogen induces RAD51C expression and localization to sites of DNA damage
Abstract
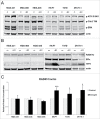
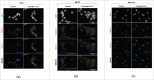
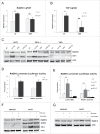
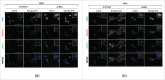
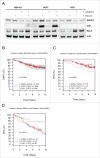
Homologous recombination (HR) is a conserved process that maintains genome stability and cell survival by repairing DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs). The RAD51-related family of proteins is involved in repair of DSBs; consequently, deregulation of RAD51 causes chromosomal rearrangements and stimulates tumorigenesis. RAD51C has been identified as a potential tumor suppressor and a breast and ovarian cancer susceptibility gene. Recent studies have also implicated estrogen as a DNA-damaging agent that causes DSBs. We found that in ERα-positive breast cancer cells, estrogen transcriptionally regulates RAD51C expression in ERα-dependent mechanism. Moreover, estrogen induces RAD51C assembly into nuclear foci at DSBs, which is a precursor to RAD51 complex recruitment to the nucleus. Additionally, disruption of ERα signaling by either anti-estrogens or siRNA prevented estrogen induced upregulation of RAD51C. We have also found an association of a worse clinical outcome between RAD51C expression and ERα status of tumors. These findings provide insight into the mechanism of genomic instability in ERα-positive breast cancer and suggest that individuals with mutations in RAD51C that are exposed to estrogen would be more susceptible to accumulation of DNA damage, leading to cancer progression.
Keywords: DNA double-strand break repair; ERα; RAD51C; breast cancer; estrogen.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Interplay between the Cellular Response to DNA Double-Strand Breaks and Estrogen.Cells. 2022 Oct 1;11(19):3097. doi: 10.3390/cells11193097. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36231059 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Estrogen receptor α-mediated transcription induces cell cycle-dependent DNA double-strand breaks.Carcinogenesis. 2011 Mar;32(3):279-85. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgq255. Epub 2010 Nov 26. Carcinogenesis. 2011. PMID: 21112959
-
Interplay between human DNA repair proteins at a unique double-strand break in vivo.EMBO J. 2006 Jan 11;25(1):222-31. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600914. Epub 2006 Jan 5. EMBO J. 2006. PMID: 16395335 Free PMC article.
-
RAD51C: a novel cancer susceptibility gene is linked to Fanconi anemia and breast cancer.Carcinogenesis. 2010 Dec;31(12):2031-8. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgq210. Epub 2010 Oct 15. Carcinogenesis. 2010. PMID: 20952512 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interaction of the double-strand break repair kinase DNA-PK and estrogen receptor-alpha.Mol Biol Cell. 2010 May 1;21(9):1620-8. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e09-08-0724. Epub 2010 Mar 10. Mol Biol Cell. 2010. PMID: 20219974 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Moderate-Risk Genes for Hereditary Ovarian Cancers Involved in the Homologous Recombination Repair Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 4;23(19):11790. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911790. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36233090 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Estrogen receptor α promotes protein synthesis by fine-tuning the expression of the eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3 subunit f (eIF3f).J Biol Chem. 2019 Feb 15;294(7):2267-2278. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.004383. Epub 2018 Dec 20. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30573685 Free PMC article.
-
Fanconi anemia and mTOR pathways functionally interact during stalled replication fork recovery.FEBS Lett. 2021 Mar;595(5):595-603. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.14035. Epub 2021 Jan 28. FEBS Lett. 2021. PMID: 33423298 Free PMC article.
-
Novel frontiers in urogenital cancers: from molecular bases to preclinical models to tailor personalized treatments in ovarian and prostate cancer patients.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2024 May 15;43(1):146. doi: 10.1186/s13046-024-03065-0. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38750579 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Interplay between the Cellular Response to DNA Double-Strand Breaks and Estrogen.Cells. 2022 Oct 1;11(19):3097. doi: 10.3390/cells11193097. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36231059 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ciccia A, Elledge SJ. The DNA damage response: making it safe to play with knives. Mol Cell 2010; 40:179-204; PMID:20965415; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2010.09.019 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jackson SP, Bartek J. The DNA-damage response in human biology and disease. Nature 2009; 461:1071-8; PMID:19847258; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature08467 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Narod SA, Foulkes WD. BRCA1 and BRCA2: 1994 and beyond. Nat Rev Cancer 2004; 4:665-76; PMID:15343273; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nrc1431 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Khanna KK, Jackson SP. DNA double-strand breaks: signaling, repair and the cancer connection. Nat Genet 2001; 27:247-54; PMID:11242102; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/85798 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Venkitaraman AR. Cancer susceptibility and the functions of BRCA1 and BRCA2. Cell 2002; 108:171-82; PMID:11832208; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8674(02)00615-3 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
