Bronchiectasis and other chronic lung diseases in adolescents living with HIV
- PMID: 27753690
- PMCID: PMC5408733
- DOI: 10.1097/QCO.0000000000000325
Bronchiectasis and other chronic lung diseases in adolescents living with HIV
Abstract
Purpose of review: The incidence of pulmonary infections has declined dramatically with improved access to antiretroviral therapy (ART) and cotrimoxazole prophylaxis, but chronic lung disease (CLD) is an increasingly recognized but poorly understood complication in adolescents with perinatally acquired HIV.
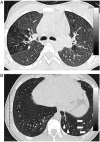
Recent findings: There is a high prevalence of chronic respiratory symptoms, abnormal spirometry and chest radiographic abnormalities among HIV-infected adolescents in sub-Saharan Africa, wherein 90% of the world's HIV-infected children live. The incidence of lymphocytic interstitial pneumonitis, the most common cause of CLD in the pre-ART era, has declined with increased ART access. Small airways disease, particularly constrictive obliterative bronchiolitis and bronchiectasis, are emerging as leading causes of CLD among HIV-infected adolescents in low-income and middle-income countries. Asthma may be more common in high-income settings. Likely risk factors for CLD include recurrent pulmonary infections, air pollution, HIV-related immune dysfunction, and untreated HIV infection, particularly during critical stages of lung development.
Summary: Globally, the importance of HIV-associated CLD as a cause of morbidity and mortality is increasing, especially as survival has improved dramatically with ART and growing numbers of children living with HIV enter adolescence. Further research is urgently needed to elucidate the natural history and pathogenesis of CLD, and to determine optimal screening, diagnostic and treatment strategies.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr Miller is a panel member for Guidelines for the Prevention and Treatment of Opportunistic Infections in HIV-infected Adults and Adolescents (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the National Institutes of Health, and the HIV Medicine Association of the Infectious Diseases Society of America) and has received honoraria from Gilead, ViiV, Merck, and Janssen for non-promotional lectures on clinical aspects of HIV infection. For the remaining authors, none were declared.
Figures
References
-
- UNAIDS. Global Report: UNAIDS report on the global AIDS epidemic 2013. Geneva. 2013:1–198.
-
- Grubb JR, Moorman AC, Baker RK, Masur H. The changing spectrum of pulmonary disease in patients with HIV infection on antiretroviral therapy. AIDS. 2006;20:1095–1107. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

