New Insights into Various Production Characteristics of Streptococcus thermophilus Strains
- PMID: 27754312
- PMCID: PMC5085733
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms17101701
New Insights into Various Production Characteristics of Streptococcus thermophilus Strains
Abstract
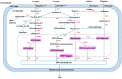
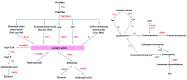
Streptococcus thermophilus is one of the most valuable homo-fermentative lactic acid bacteria, which, for a long time, has been widely used as a starter for the production of fermented dairy products. The key production characteristics of S. thermophilus, for example the production of extracellular polysaccharide, proteolytic enzymes and flavor substances as well as acidifying capacity etc., have an important effect on the quality of dairy products. The acidification capacity of the strains determines the manufacturing time and quality of dairy products. It depends on the sugar utilization ability of strains. The production of extracellular polysaccharide is beneficial for improving the texture of dairy products. Flavor substances increase the acceptability of dairy products. The proteolytic activity of the strain influences not only the absorption of the nitrogen source, but also the formation of flavor substances. Different strains have obvious differences in production characteristics via long-time evolution and adaptation to environment. Gaining new strains with novel and desirable characteristics is an important long-term goal for researchers and the fermenting industry. The understanding of the potential molecular mechanisms behind important characteristics of different strains will promote the screening and breeding of excellent strains. In this paper, key technological and functional properties of different S. thermophilus strains are discussed, including sugar metabolism, proteolytic system and amino acid metabolism, and polysaccharide and flavor substance biosynthesis. At the same time, diversity of genomes and plasmids of S. thermophilus are presented. Advances in research on key production characteristics and molecular levels of S. thermophilus will increase understanding of molecular mechanisms of different strains with different important characteristics, and improve the industrialization control level for fermented foods.
Keywords: Streptococcus thermophilus; genomics; plasmid; production characteristics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Technological properties assessment and two component systems distribution of Streptococcus thermophilus strains isolated from fermented milk.Arch Microbiol. 2018 May;200(4):567-580. doi: 10.1007/s00203-017-1468-9. Epub 2017 Dec 13. Arch Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29236144
-
Biofilm Formation on Stainless Steel by Streptococcus thermophilus UC8547 in Milk Environments Is Mediated by the Proteinase PrtS.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2017 Mar 31;83(8):e02840-16. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02840-16. Print 2017 Apr 15. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28159787 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a milk-based medium for the selection of urease-defective mutants of Streptococcus thermophilus.Int J Food Microbiol. 2019 Nov 2;308:108304. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2019.108304. Epub 2019 Aug 10. Int J Food Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31425789
-
New insights in the molecular biology and physiology of Streptococcus thermophilus revealed by comparative genomics.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2005 Aug;29(3):435-63. doi: 10.1016/j.femsre.2005.04.008. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2005. PMID: 16125007 Review.
-
New advances in exopolysaccharides production of Streptococcus thermophilus.Arch Microbiol. 2017 Aug;199(6):799-809. doi: 10.1007/s00203-017-1366-1. Epub 2017 Mar 29. Arch Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28357474 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparison of gal-lac operons in wild-type galactose-positive and -negative Streptococcus thermophilus by genomics and transcription analysis.J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019 May;46(5):751-758. doi: 10.1007/s10295-019-02145-x. Epub 2019 Feb 4. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 30715626
-
Lysates from the probiotic bacterium Streptococcus thermophilus enhances the survival of T cells and triggers programmed cell death in neuroblastoma cells.Med Oncol. 2023 Oct 3;40(11):315. doi: 10.1007/s12032-023-02186-4. Med Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37787808
-
High-quality-draft genome sequence of the multiple heavy metal resistant bacterium Pseudaminobacter manganicus JH-7T.Stand Genomic Sci. 2018 Oct 25;13:29. doi: 10.1186/s40793-018-0330-2. eCollection 2018. Stand Genomic Sci. 2018. PMID: 30386456 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the Sortase A in the Release of Cell-Wall Proteinase PrtS in the Growth Medium of Streptococcus thermophilus 4F44.Microorganisms. 2021 Nov 18;9(11):2380. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9112380. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 34835505 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-based approach to evaluate the metabolic potentials and exopolysaccharides production of Bacillus paralicheniformis CamBx3 isolated from a Chilean hot spring.Front Microbiol. 2024 Apr 2;15:1377965. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1377965. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38628868 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adolfsson O., Meydani S.N., Russell R.M. Yogurt and gut function. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004;80:245–256. - PubMed
-
- Iyer R., Tomar S.K., Maheswari T.U., Singh R. Streptococcus thermophilus strains: Multifunctional lactic acid bacteria. Int. Dairy J. 2010;20:133–141. doi: 10.1016/j.idairyj.2009.10.005. - DOI
-
- Vaningelgem F., Zamfir M., Mozzi F., Adriany T., Vancanneyt M. Biodiversity of exopolysaccharides produced by Streptococcus thermophilus strains is reflected in their production and their molecular and functional characteristics. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004;70:900–912. doi: 10.1128/AEM.70.2.900-912.2004. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hols P., Hancy F., Fontaine L., Grossiord B., Prozzi D. New insights in the molecular biology and physiology of Streptococcus thermophilus revealed by comparative genomics. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2005;29:435–463. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

