Distribution, Pest Status and Fungal Associates of Euwallacea nr. fornicatus in Florida Avocado Groves
- PMID: 27754408
- PMCID: PMC5198203
- DOI: 10.3390/insects7040055
Distribution, Pest Status and Fungal Associates of Euwallacea nr. fornicatus in Florida Avocado Groves
Abstract
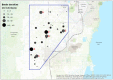
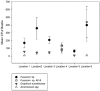
Members of a complex of cryptic species, that correspond morphologically to the ambrosia beetle Euwallacea fornicatus (Eichhoff) (Coleoptera: Curculionidae: Scolytinae), were recently found attacking avocado (Persea americana Mill.) in Israel and California. In early 2016, an outbreak of another member of this species complex was detected infesting approximately 1500 avocado trees in an avocado orchard at Homestead, Florida. An area-wide survey was conducted in commercial avocado groves of Miami-Dade County, Florida to determine the distribution and abundance of E. nr. fornicatus, to identify different populations of E. nr. fornicatus and their fungal associates, and to assess the extent of damage to avocado trees. Ewallacea nr. fornicatus were captured in 31 of the 33 sampled sites. A sample of 35 beetles from six different locations was identified as E. nr. fornicatus sp. #2, which is genetically distinct from the species causing damage in California and Israel. Eleven fungal associates were identified: an unknown Fusarium sp., AF-8, AF-6, Graphium euwallaceae, Acremonium sp. Acremonium morum, Acremonium masseei, Elaphocordyceps sp. and three yeast species. The unknown Fusarium isolates were the most abundant and frequently found fungus species associated with adult beetles and lesions surrounding the beetle galleries. In addition to fungal associates, three bacteria species were found associated with adult E. nr. fornicatus. Visual inspections detected significant damage in only two orchards. A large number of beetles were captured in locations with no apparent damage on the avocado trees suggesting that E. nr. fornicatus are associated with other host(s) outside the groves or with dead trees or branches inside the groves. More research is needed to determine the potential threat E. nr. fornicatus and its fungal associates pose to the avocado industry and agricultural and natural ecosystems in Florida.
Keywords: Fusarium; ambrosia beetles; symbiosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of Trap Designs for Detection of Euwallacea nr. fornicatus and Other Scolytinae (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) That Vector Fungal Pathogens of Avocado Trees in Florida.J Econ Entomol. 2020 Apr 6;113(2):980-987. doi: 10.1093/jee/toz311. J Econ Entomol. 2020. PMID: 31742602
-
Fusarium euwallaceae sp. nov.--a symbiotic fungus of Euwallacea sp., an invasive ambrosia beetle in Israel and California.Mycologia. 2013 Nov-Dec;105(6):1595-606. doi: 10.3852/13-066. Epub 2013 Aug 8. Mycologia. 2013. PMID: 23928415
-
α-Copaene is an attractant, synergistic with quercivorol, for improved detection of Euwallacea nr. fornicatus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae: Scolytinae).PLoS One. 2017 Jun 13;12(6):e0179416. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0179416. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28609448 Free PMC article.
-
Two Novel Fungal Symbionts Fusarium kuroshium sp. nov. and Graphium kuroshium sp. nov. of Kuroshio Shot Hole Borer (Euwallacea sp. nr. fornicatus) Cause Fusarium Dieback on Woody Host Species in California.Plant Dis. 2018 Jun;102(6):1154-1164. doi: 10.1094/PDIS-07-17-1042-RE. Epub 2018 Apr 2. Plant Dis. 2018. PMID: 30673440
-
Reproduction and Control of the Invasive Polyphagous Shot Hole Borer, Euwallacea nr. fornicatus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae: Scolytinae), in Three Species of Hardwoods: Effective Sanitation Through Felling and Chipping.Environ Entomol. 2020 Oct 17;49(5):1155-1163. doi: 10.1093/ee/nvaa103. Environ Entomol. 2020. PMID: 32885817 Review.
Cited by
-
Spatial Analysis of Presence, Injury, and Economic Impact of the Melolonthidae (Coleoptera: Scarabaeoidea) Complex in Avocado Crops.Neotrop Entomol. 2019 Aug;48(4):583-593. doi: 10.1007/s13744-019-00685-6. Epub 2019 Jun 3. Neotrop Entomol. 2019. PMID: 31161584
-
Flexibility in the ambrosia symbiosis of Xyleborus bispinatus.Front Microbiol. 2023 Mar 2;14:1110474. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1110474. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36937297 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation and Identification of Pennogenin Tetraglycoside from Cestrum nocturnum (Solanaceae) and Its Antifungal Activity against Fusarium kuroshium, Causal Agent of Fusarium Dieback.Molecules. 2022 Mar 13;27(6):1860. doi: 10.3390/molecules27061860. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35335224 Free PMC article.
-
Diffusible and volatile organic compounds produced by avocado rhizobacteria exhibit antifungal effects against Fusarium kuroshium.Braz J Microbiol. 2020 Sep;51(3):861-873. doi: 10.1007/s42770-020-00249-6. Epub 2020 Mar 12. Braz J Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32166656 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory Effects of Semiochemicals on the Attraction of an Ambrosia Beetle Euwallacea nr. fornicatus to Quercivorol.J Chem Ecol. 2018 Jun;44(6):565-575. doi: 10.1007/s10886-018-0959-8. Epub 2018 Apr 17. J Chem Ecol. 2018. PMID: 29663165
References
-
- Carrillo D., Duncan R.E., Ploetz J.N., Campbell A.F., Ploetz R.C., Peña J.E. Lateral transfer of a phytopathogenic symbiont among native and exotic ambrosia beetles. Plant Pathol. 2014;63:54–62. doi: 10.1111/ppa.12073. - DOI
-
- O’Donnell K., Sink S., Ran L.H.R., Hulcr J., Kasson M.T., Ploetz C.R., Konkol J.L., Ploetz J.N., Carrillo D., Campbell A., et al. Discordant phylogenies suggest repeated host shifts in the Fusarium–Euwallacea ambrosia beetle mutualism. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2015;82:277–290. doi: 10.1016/j.fgb.2014.10.014. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mendel Z., Protasov A., Sharon M., Zveibil A., Yehuda S.B., O’Donnell K., Rabaglia R., Wysoki M., Freeman S. An Asian ambrosia beetle Euwallacea fornicatus and its novel symbiotic fungus Fusarium sp. pose a serious threat to the Israeli avocado industry. Phytoparasitica. 2012;40:235–238. doi: 10.1007/s12600-012-0223-7. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

