UBXD Proteins: A Family of Proteins with Diverse Functions in Cancer
- PMID: 27754413
- PMCID: PMC5085755
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms17101724
UBXD Proteins: A Family of Proteins with Diverse Functions in Cancer
Abstract
The UBXD family is a diverse group of UBX (ubiquitin-regulatory X) domain-containing proteins in mammalian cells. Members of this family contain a UBX domain typically located at the carboxyl-terminal of the protein. In contrast to the UBX domain shared by all members of UBXD family, the amino-terminal domains are diverse and appear to carry out different roles in a subcellular localization-dependent manner. UBXD proteins are principally associated with the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), where they positively or negatively regulate the ER-associated degradation machinery (ERAD). The distinct protein interaction networks of UBXD proteins allow them to have specific functions independent of the ERAD pathway in a cell type- and tissue context-dependent manner. Recent reports have illustrated that a number of mammalian members of the UBXD family play critical roles in several proliferation and apoptosis pathways dysregulated in selected types of cancer. This review covers recent advances that elucidate the therapeutic potential of selected members of the UBXD family that can contribute to tumor growth.
Keywords: UBXD family; animal models; apoptosis; cell proliferation; targeted therapy; tumor; xenografts.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
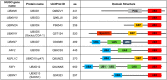
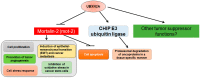
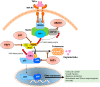

Similar articles
-
Systematic proteomics of the VCP-UBXD adaptor network identifies a role for UBXN10 in regulating ciliogenesis.Nat Cell Biol. 2015 Oct;17(10):1356-69. doi: 10.1038/ncb3238. Epub 2015 Sep 21. Nat Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 26389662 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the role of ubiquitin regulatory X domain family proteins in cancers: bioinformatics insights, mechanisms, and implications for therapy.J Transl Med. 2024 Feb 15;22(1):157. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-04890-9. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38365777 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional characterization of the plant ubiquitin regulatory X (UBX) domain-containing protein AtPUX7 in Arabidopsis thaliana.Gene. 2013 Sep 10;526(2):299-308. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2013.05.056. Epub 2013 Jun 4. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23747397
-
The opposite role of two UBA-UBX containing proteins, p47 and SAKS1 in the degradation of a single ERAD substrate, α-TCR.Mol Cell Biochem. 2017 Jan;425(1-2):37-45. doi: 10.1007/s11010-016-2860-5. Epub 2016 Oct 26. Mol Cell Biochem. 2017. PMID: 27785701
-
Endoplasmic reticulum quality control in cancer: Friend or foe.Semin Cancer Biol. 2015 Aug;33:25-33. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2015.02.003. Epub 2015 Mar 18. Semin Cancer Biol. 2015. PMID: 25794824 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
UBXN11 Predicts as a Poor Index for Colorectal Cancer and Contributes to the Tumorigenesis by Activating NF-κB Signaling.Dig Dis Sci. 2024 Jun;69(6):2074-2082. doi: 10.1007/s10620-024-08414-9. Epub 2024 Apr 15. Dig Dis Sci. 2024. PMID: 38622461
-
The AAA + ATPase valosin-containing protein (VCP)/p97/Cdc48 interaction network in Leishmania.Sci Rep. 2020 Aug 4;10(1):13135. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-70010-4. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32753747 Free PMC article.
-
High Expression of Fas-Associated Factor 1 Indicates a Poor Prognosis in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer.Curr Oncol. 2023 Oct 25;30(11):9484-9500. doi: 10.3390/curroncol30110687. Curr Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37999107 Free PMC article.
-
A fungal core effector exploits the OsPUX8B.2-OsCDC48-6 module to suppress plant immunity.Nat Commun. 2024 Mar 22;15(1):2559. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-46903-7. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38519521 Free PMC article.
-
Domain Organization of the UBX Domain Containing Protein 9 and Analysis of Its Interactions With the Homohexameric AAA + ATPase p97 (Valosin-Containing Protein).Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Sep 23;9:748860. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.748860. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34631722 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rijal R., Arhzaouy K., Strucksberg K.H., Cross M., Hofmann A., Schroder R., Clemen C.S., Eichinger L. Mutant p97 exhibits species-specific changes of its ATPase activity and compromises the UBXD9-mediated monomerisation of p97 hexamers. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2016;95:195–207. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2016.03.004. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

