YM155 inhibits topoisomerase function
- PMID: 27754993
- PMCID: PMC5225247
- DOI: 10.1097/CAD.0000000000000441
YM155 inhibits topoisomerase function
Abstract
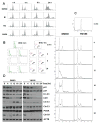
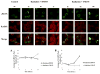
YM155 (sepantronium bromide) has been evaluated in clinical trials as a survivin suppressant, but despite positive signals from early work, later studies were negative. Clarification of the mechanism of action of YM155 is important for its further development. YM155 affects cells in a cell cycle-specific manner. When cells are in G1, YM155 prevented their progression through the S phase, leaving the cells at G1/S when exposed to YM155. Passage through mitosis from G2 is also defective following YM155 exposure. In this study, YM155 did not behave like a typical DNA intercalator in viscosity, circular dichroism, and absorption spectroscopy studies. In addition, molecular modeling experiments ruled out YM155 DNA interaction to produce DNA intercalation. We show that YM155 inhibited topoisomerase 2α decatenation and topoisomerase 1-mediated cleavage of DNA, suggesting that YM155 inhibits the enzyme function. Consistent with these findings, DNA double-strand break repair was also inhibited by YM155.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Effect of Sepatronium Bromide (YM-155) on DNA Double-Strand Breaks Repair in Cancer Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 11;21(24):9431. doi: 10.3390/ijms21249431. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33322336 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The mechanism of radiosensitization by YM155, a novel small molecule inhibitor of survivin expression, is associated with DNA damage repair.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;37(3):1219-30. doi: 10.1159/000430245. Epub 2015 Sep 30. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015. PMID: 26418254
-
YM155 sensitizes non-small cell lung cancer cells to EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitors through the mechanism of autophagy induction.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2018 Dec;1864(12):3786-3798. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2018.10.015. Epub 2018 Oct 10. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2018. PMID: 30315932
-
YM155 and BIRC5 downregulation induce genomic instability via autophagy-mediated ROS production and inhibition in DNA repair.Pharmacol Res. 2021 Apr;166:105474. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105474. Epub 2021 Feb 5. Pharmacol Res. 2021. PMID: 33549731
-
Marked anti-tumour activity of the combination of YM155, a novel survivin suppressant, and platinum-based drugs.Br J Cancer. 2010 Jun 29;103(1):36-42. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6605713. Epub 2010 Jun 1. Br J Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20517311 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Survivin Expression Is Differentially Regulated by a Selective Cross-talk between RBM38 and miRNAs let-7b or miR-203a.Cancer Res. 2021 Apr 1;81(7):1827-1839. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-20-3157. Epub 2021 Jan 20. Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 33472892 Free PMC article.
-
Ym155 Induces Oxidative Stress-Mediated DNA Damage and Cell Cycle Arrest, and Causes Programmed Cell Death in Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 16;22(4):1961. doi: 10.3390/ijms22041961. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33669447 Free PMC article.
-
Cell death in glioblastoma and the central nervous system.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2025 Apr;48(2):313-349. doi: 10.1007/s13402-024-01007-8. Epub 2024 Nov 6. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2025. PMID: 39503973 Free PMC article. Review.
-
YM155 sensitizes HeLa cells to TRAIL-mediated apoptosis via cFLIP and survivin downregulation.Oncol Lett. 2020 Oct;20(4):72. doi: 10.3892/ol.2020.11933. Epub 2020 Jul 30. Oncol Lett. 2020. PMID: 32863905 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Sepatronium Bromide (YM-155) on DNA Double-Strand Breaks Repair in Cancer Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 11;21(24):9431. doi: 10.3390/ijms21249431. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33322336 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Champoux JJ. DNA topoisomerases: structure, function, and mechanism. Annual review of biochemistry. 2001;70:369–413. - PubMed
-
- Streltsov SA. Action models for the antitumor drug camptothecin: formation of alkali-labile complex with DNA and inhibition of human DNA topoisomerase I. Journal of biomolecular structure & dynamics. 2002;20(3):447–454. - PubMed
-
- Kaufmann SH. Cell death induced by topoisomerase-targeted drugs: more questions than answers. Biochimica et biophysica acta. 1998;1400(1–3):195–211. - PubMed
-
- Tewey KM, Rowe TC, Yang L, Halligan BD, Liu LF. Adriamycin-induced DNA damage mediated by mammalian DNA topoisomerase II. Science. 1984;226(4673):466–468. - PubMed
-
- Chen GL, Yang L, Rowe TC, Halligan BD, Tewey KM, Liu LF. Nonintercalative antitumor drugs interfere with the breakage-reunion reaction of mammalian DNA topoisomerase II. The Journal of biological chemistry. 1984;259(21):13560–13566. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

