Clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis of resected cases of carcinoid tumors of the lung
- PMID: 27755793
- PMCID: PMC5093170
- DOI: 10.1111/1759-7714.12377
Clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis of resected cases of carcinoid tumors of the lung
Abstract
Background: Lung carcinoid tumors are rare, low-grade, malignant neoplasms with some unclear features. The aim of this study was to analyze clinicopathological features and long-term survival in patients with primary lung carcinoid tumors.
Methods: Patients who underwent surgery in our clinic and were diagnosed with carcinoid tumors, between August 1997 and July 2012, were included in the study. Patient characteristics and clinicopathological factors were retrospectively evaluated.
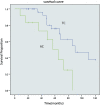
Results: Bronchial carcinoids comprised only 1.0% of lung cancer cases treated by resection. They are classified into two distinct categories: typical carcinoid (TC) and atypical carcinoid (AC) tumors. AC tumors occurred more frequently in younger patients and in smokers, and had a poorer prognosis than TC tumors. Overall three and five-year survival rates for TC and AC were 92.6% and 81.1%, respectively. Univariate analysis showed that tumor size ( P = 0.012) and histological type ( P = 0.013) are prognostic factors. Multivariate analysis revealed that only tumor size ( P = 0.044) was an independent prognostic factor.
Conclusions: The prognosis for bronchial carcinoid tumors was better than other types of lung cancer and TC was significantly better than AC. Radical lymph node dissection was the best treatment, with complete removal of the tumor. Tumor size was an independent prognostic factor for bronchial carcinoid tumors.
Keywords: Carcinoid; lung cancer; surgery.
© 2016 The Authors. Thoracic Cancer published by China Lung Oncology Group and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Rodriguez JA, Meyers MO, Jacome TH, Failla P, Harrison LH Jr. Intraoperative detection of a bronchial carcinoid with a radiolabeled somatostatin analog. Chest 2002; 121: 985–8. - PubMed
-
- Kosmidis PA. Treatment of carcinoid of the lung. Curr Opin Oncol 2004; 16: 146–9. - PubMed
-
- Travis WD, Rush W, Flieder DB et al Survival analysis of 200 pulmonary neuroendocrine tumors with clarification of criteria for atypical carcinoid and its separation from typical carcinoid. Am J Surg Pathol 1998; 22: 934–44. - PubMed
-
- Zhong CX, Yao F, Zhao H, Shi JX, Fan LM. Long‐term outcomes of surgical treatment for pulmonary carcinoid tumors: 20 years’ experience with 131 patients. Chin Med J (Engl) 2012; 125: 3022–6. - PubMed
-
- Gustafsson BI, Kidd M, Chan A, Malfertheiner MV, Modlin IM. Bronchopulmonary neuroendocrine tumors. Cancer 2008; 113: 5–21. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical