A thiadiazole reduces the virulence of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae by inhibiting the histidine utilization pathway and quorum sensing
- PMID: 27756112
- PMCID: PMC6638098
- DOI: 10.1111/mpp.12503
A thiadiazole reduces the virulence of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae by inhibiting the histidine utilization pathway and quorum sensing
Abstract
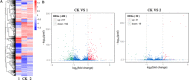
Thiazole, isothiazole, thiadiazole and their derivatives are widely thought to induce host defences against plant pathogens. In this article, we report that bismerthiazol, a thiadiazole molecule, reduces disease by inhibiting the histidine utilization (Hut) pathway and quorum sensing (QS). Bismerthiazol provides excellent control of bacterial rice leaf blight (BLB) caused by Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae (Xoo), but does not greatly inhibit Xoo growth in vitro. According to RNA-sequencing analysis, the transcription of the Hut pathway genes of Xoo ZJ173 was inhibited after 4.5 and 9.0 h of bismerthiazol treatment. Functional studies of hutG and hutU indicated that the Hut pathway had little effect on the growth and bismerthiazol sensitivity of Xoo in vitro, but significantly reduced the aggregation of Xoo cells. Deletion mutants of hutG or hutU were more motile, produced less biofilm and were less virulent than the wild-type, indicating that the Hut pathway is involved in QS and contributes to virulence. The overexpression of the hutG-U operons in ZJ173 reduced Xoo control by bismerthiazol. Bismerthiazol did not inhibit the transcription of Hut pathway genes, QS or virulence of the bismerthiazol-resistant strain 2-1-1. The results indicate that bismerthiazol reduces Xoo virulence by inhibiting the Hut pathway and QS.
Keywords: Hut pathway; QS; Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae; bismerthiazol; rice; thiadiazole; virulence.
© 2016 BSPP AND JOHN WILEY & SONS LTD.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Two thiadiazole compounds promote rice defence against Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae by suppressing the bacterium's production of extracellular polysaccharides.Mol Plant Pathol. 2015 Oct;16(8):882-92. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12248. Epub 2015 Apr 19. Mol Plant Pathol. 2015. PMID: 25727092 Free PMC article.
-
Photochemical degradation of bismerthiazol: structural characterisation of the photoproducts and their inhibitory activities against Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae.Pest Manag Sci. 2016 May;72(5):997-1003. doi: 10.1002/ps.4080. Epub 2015 Aug 11. Pest Manag Sci. 2016. PMID: 26174501
-
ATP-Dependent Protease ClpP and Its Subunits ClpA, ClpB, and ClpX Involved in the Field Bismerthiazol Resistance in Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae.Phytopathology. 2021 Nov;111(11):2030-2040. doi: 10.1094/PHYTO-01-21-0011-R. Epub 2021 Nov 19. Phytopathology. 2021. PMID: 33973800
-
Screening and characterization of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae strains with resistance to pheazine-1-carboxylic acid.Pestic Biochem Physiol. 2018 Feb;145:8-14. doi: 10.1016/j.pestbp.2017.12.003. Epub 2017 Dec 18. Pestic Biochem Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29482735
-
Cross-Talk Signaling in Rice During Combined Drought and Bacterial Blight Stress.Front Plant Sci. 2019 Mar 6;10:193. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.00193. eCollection 2019. Front Plant Sci. 2019. PMID: 30894866 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Specific High Toxicity of Xinjunan (Dioctyldiethylenetriamine) to Xanthomonas by Affecting the Iron Metabolism.Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Mar 6;11(2):e0438222. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.04382-22. Online ahead of print. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 36877068 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the Abilities of Three Kinds of Copper-Based Nanoparticles to Control Kiwifruit Bacterial Canker.Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Jul 4;11(7):891. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11070891. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35884145 Free PMC article.
-
Antibacterial and biofilm inhibition activity of biofabricated silver nanoparticles against Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae causing blight disease of rice instigates disease suppression.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020 Mar 16;36(4):55. doi: 10.1007/s11274-020-02826-1. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32180020
-
Global Regulator PhoP is Necessary for Motility, Biofilm Formation, Exoenzyme Production and Virulence of Xanthomonas citri Subsp. citri on Citrus Plants.Genes (Basel). 2019 May 6;10(5):340. doi: 10.3390/genes10050340. Genes (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31064142 Free PMC article.
-
On the use of antibiotics to control plant pathogenic bacteria: a genetic and genomic perspective.Front Microbiol. 2023 Jun 27;14:1221478. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1221478. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37440885 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Antoine, R. and Locht, C. (1992) Isolation and molecular characterization of a novel broad‐host‐range plasmid from Bordetella bronchiseptica with sequence similarities to plasmids from gram‐positive organisms. Mol. Microbiol. 6, 1785–1799. - PubMed
-
- Antonijevic, M. and Petrovic, M. (2008) Copper corrosion inhibitors. A review. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 3, 1–28.
-
- Barber, C. , Tang, J. , Feng, J. , Pan, M. , Wilson, T. , Slater, H. , Dow, J.M. , Williams, P. and Daniels, M.J. (1997) A novel regulatory system required for pathogenicity of Xanthomonas campestris is mediated by a small diffusible signal molecule. Mol. Microbiol. 24, 555–566. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

