Malaria burden in a birth cohort of HIV-exposed uninfected Ugandan infants living in a high malaria transmission setting
- PMID: 27756308
- PMCID: PMC5070200
- DOI: 10.1186/s12936-016-1568-z
Malaria burden in a birth cohort of HIV-exposed uninfected Ugandan infants living in a high malaria transmission setting
Abstract
Background: HIV-exposed, uninfected (HEU) infants suffer high morbidity and mortality in the first year of life compared to HIV-unexposed, uninfected (HUU) infants, but accurate data on the contribution of malaria are limited.
Methods: The incidence of febrile illnesses and malaria were evaluated in a birth cohort of HEU infants. Infants were prescribed daily trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (TS) prophylaxis from 6 weeks of age until exclusion of HIV-infection after cessation of breastfeeding. Infants were followed for all illnesses using passive surveillance and routine blood smears were done monthly. Malaria was diagnosed as a positive blood smear plus fever. Placental malaria was determined by histopathology, placental blood smear and PCR. Risk factors for time to first episode of malaria were assessed using a Cox proportional hazards model. Malaria incidence among HEU infants aged 6-12 months was compared to that in other cohorts of HEU and HUU infants from the same region.
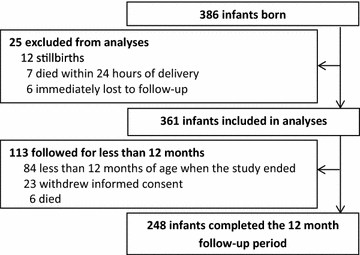
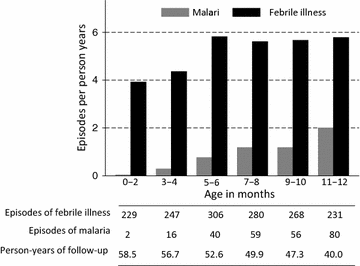
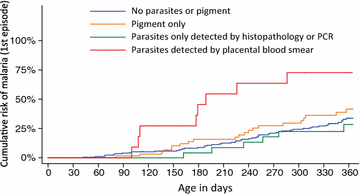
Results: Among 361 HEU infants enrolled, 248 completed 12 months of follow-up resulting in 1562 episodes of febrile illness and 253 episodes of malaria after 305 person-years of follow-up. The incidence of febrile illness was 5.12 episodes per person-year (PPY), ranging from 4.13 episodes PPY in the first 4 months of life to 5.71 episodes PPY between 5 and 12 months of age. The overall malaria incidence was 0.83 episodes per person-year (PPY), increasing from 0.03 episodes PPY in the first 2 months of life to 2.00 episodes PPY between 11 and 12 months of age. There were no episodes of complicated malaria. The prevalence of asymptomatic parasitaemia was 1.2 % (19 of 1568 routine smears positive). Infants born to mothers with parasites detected from placental blood smears were at higher risk of malaria (hazard ratio = 4.51, P < 0.001). HEU infants in this study had a 2.4- to 3.5-fold lower incidence of malaria compared to HUU infants in other cohort studies from the same area.
Conclusion: The burden of malaria in this birth cohort of HEU infants living in a high-transmission setting and taking daily TS prophylaxis was relatively low. Alternative etiologies of fever should be considered in HEU-infants taking daily TS prophylaxis who present with fever. Trial Registration NCT00993031, registered 8 October, 2009.
Keywords: HIV-exposed uninfected infants; Malaria; Placental malaria.
Figures
References
-
- Koyanagi A, Humphrey JH, Ntozini R, Nathoo K, Moulton LH, Iliff P, et al. Morbidity among human immunodeficiency virus-exposed but uninfected, human immunodeficiency virus-infected, and human immunodeficiency virus-unexposed infants in Zimbabwe before availability of highly active antiretroviral therapy. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2011;30:45–51. doi: 10.1097/INF.0b013e3181ecbf7e. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Brahmbhatt H, Kigozi G, Wabwire-Mangen F, Serwadda D, Lutalo T, Nalugoda F, et al. Mortality in HIV-infected and uninfected children of HIV-infected and uninfected mothers in rural Uganda. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1999;2006(41):504–508. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical