Size polymorphism and low sequence diversity in the locus encoding the Plasmodium vivax rhoptry neck protein 4 (PvRON4) in Colombian isolates
- PMID: 27756311
- PMCID: PMC5069803
- DOI: 10.1186/s12936-016-1563-4
Size polymorphism and low sequence diversity in the locus encoding the Plasmodium vivax rhoptry neck protein 4 (PvRON4) in Colombian isolates
Abstract
Background: Designing a vaccine against Plasmodium vivax has focused on selecting antigens involved in invasion mechanisms that must have domains with low polymorphism for avoiding allele-specific immune responses. The rhoptry neck protein 4 (RON4) forms part of the tight junction, which is essential in the invasion of hepatocytes and/or erythrocytes; however, little is known about this locus' genetic diversity.
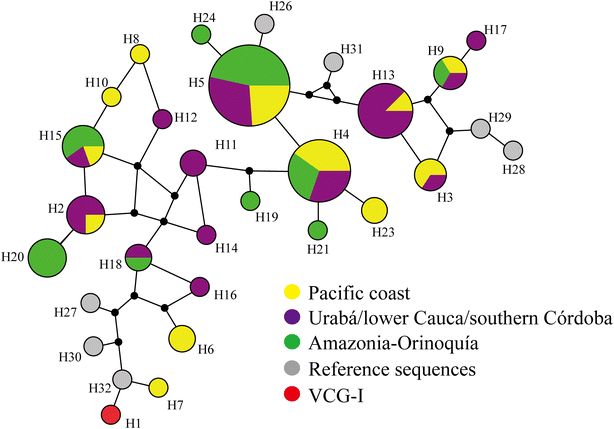
Methods: DNA sequences from 73 Colombian clinical isolates from pvron4 gene were analysed for characterizing their genetic diversity; pvron4 haplotype number and distribution, as well as the evolutionary forces determining diversity pattern, were assessed by population genetics and molecular evolutionary approaches.
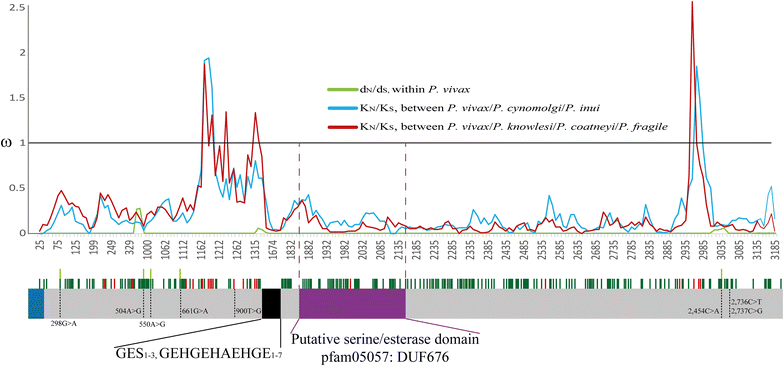
Results: ron4 has low genetic diversity in P. vivax at sequence level; however, a variable amount of tandem repeats at the N-terminal region leads to extensive size polymorphism. This region seems to be exposed to the immune system. The central region has a putative esterase/lipase domain which, like the protein's C-terminal fragment, is highly conserved at intra- and inter-species level. Both regions are under purifying selection.
Conclusions: pvron4 is the locus having the lowest genetic diversity described to date for P. vivax. The repeat regions in the N-terminal region could be associated with immune evasion mechanisms while the central region and the C-terminal region seem to be under functional or structural constraint. Bearing such results in mind, the PvRON4 central and/or C-terminal portions represent promising candidates when designing a subunit-based vaccine as they are aimed at avoiding an allele-specific immune response, which might limit vaccine efficacy.
Keywords: Functional restriction; Genetic diversity; Natural selection; Plasmodium vivax; Rhoptry; Tandem repeat; pvron4.
Figures
References
-
- Naghavi M, Wang H, Lozano R, Davis A, Liang X, Zhou M. GBD 2013 mortality and causes of death collaborators. Global, regional, and national age-sex specific all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 240 causes of death, 1990–2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet. 2015;385:117–171. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61682-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- WHO. World malaria report 2015. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2015. http://www.who.int/malaria/publications/world-malaria-report-2015/wmr201....
-
- UNICEF. Achieving the malaria MDG target. Reversing the incidence of malaria 2000–2015 http://www.unicef.org/publications/files/Achieving_the_Malaria_MDG_Targe....
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

