Esculetin induces antiproliferative and apoptotic response in pancreatic cancer cells by directly binding to KEAP1
- PMID: 27756327
- PMCID: PMC5069780
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-016-0550-2
Esculetin induces antiproliferative and apoptotic response in pancreatic cancer cells by directly binding to KEAP1
Abstract
Background: A handful of studies have exploited antitumor potential of esculetin, a dihydroxy coumarine derivative; the targets to which it binds and the possible downstream mechanism for its cytotoxicity in cancer cells remain to be elucidated. Using pancreatic cancer cell lines as a model system, herein the study was initiated to check the efficacy of esculetin in inhibiting growth of these cancer cells, to decipher mechanism of its action and to predict its direct binding target protein.
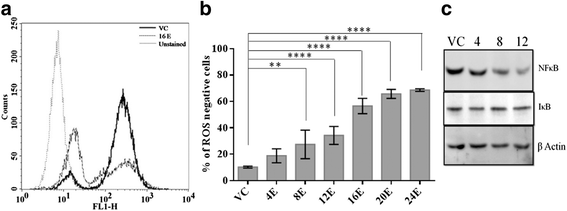
Methods: The cytotoxicity of esculetin was determined in PANC-1, MIA PaCa-2 and AsPC-1 cell lines; followed by an inspection of intracellular levels of ROS and its associated transcription factor, p65-NF-κB. The interaction between transcription factor, Nrf2 and its regulator KEAP1 was studied in the presence and absence of esculetin. The effect of Nrf2 on gene expression of antioxidant response element pathway was monitored by real time PCR. Thereafter, potential binding target of esculetin was predicted through molecular docking and then confirmed in vitro.
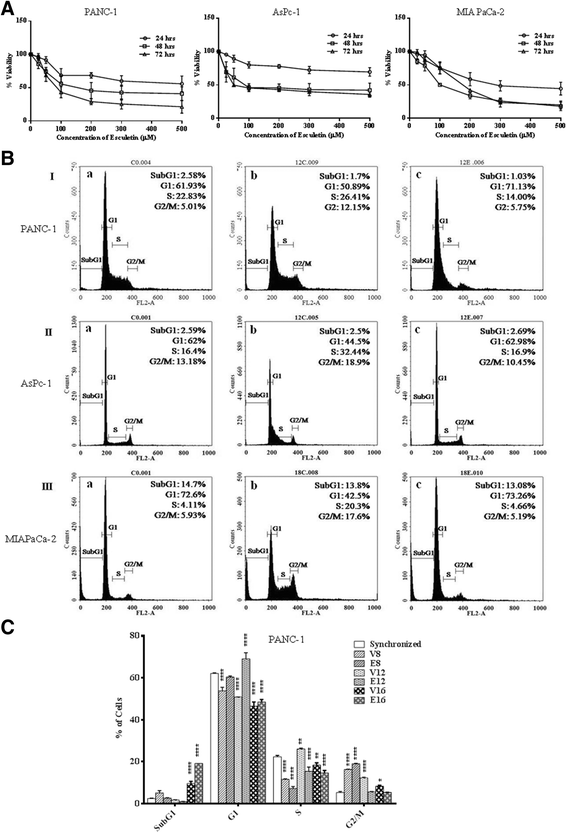
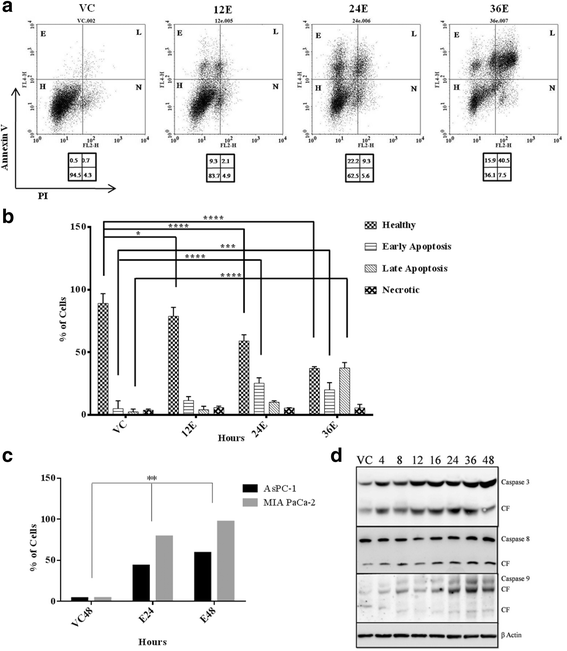
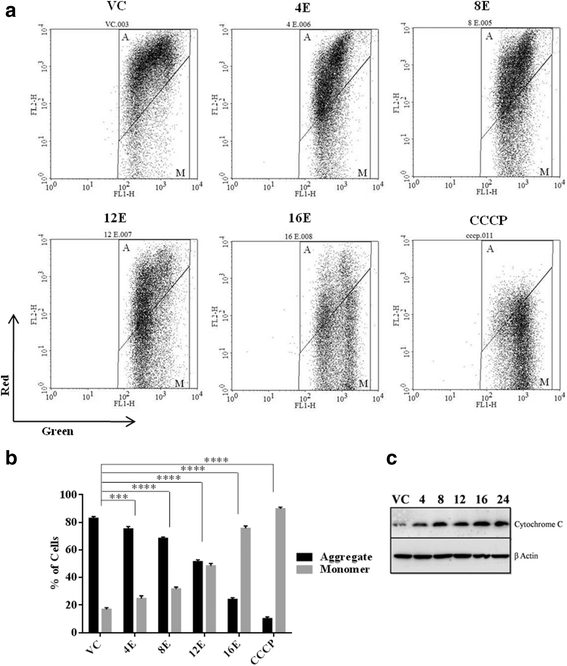
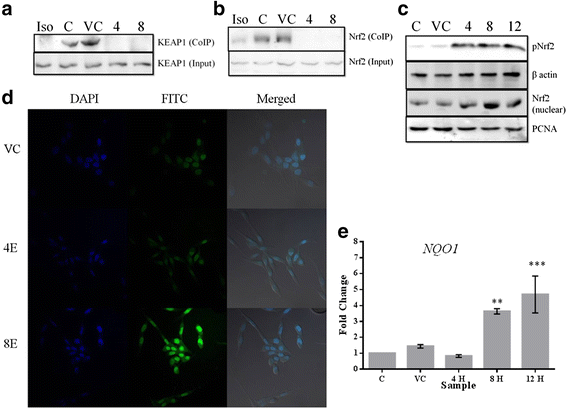
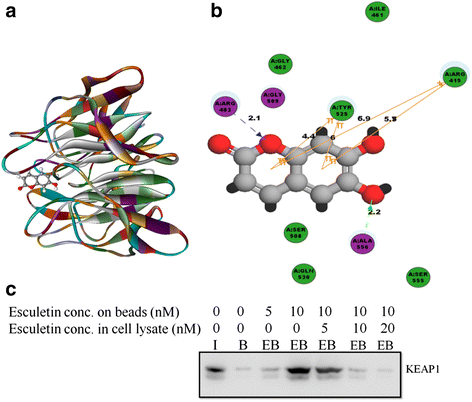
Results: Esculetin treatment in all three pancreatic cancer cell lines resulted in significant growth inhibition with G1-phase cell cycle arrest and induction of mitochondrial dependent apoptosis through activation of caspases 3, 8 and 9. A notable decrease was observed in intracellular ROS and protein levels of p65-NF-κB in PANC-1 cells on esculetin treatment. Antioxidant response regulator Nrf2 has been reportedly involved in crosstalk with NF-κB. Interaction between Nrf2 and KEAP1 was found to be lost upon esculetin treatment in PANC-1 and MIA Paca-2 cells. Nuclear accumulation of Nrf2 and an upregulation of expression of Nrf2 regulated gene NQO1, observed on esculetin treatment in PANC-1 further supported the activation of Nrf2. To account for the loss of Nrf2-KEAP1 interaction on esculetin treatment, direct binding potential between esculetin and KEAP1 was depicted in silico using molecular docking studies. Pull down assay using esculetin conjugated sepharose beads confirmed the binding between esculetin and KEAP1.
Conclusions: We propose that esculetin binds to KEAP1 and inhibits its interaction with Nrf2 in pancreatic cancer cells. This thereby promotes nuclear accumulation of Nrf2 in PANC-1 cells that induces antiproliferative and apoptotic response possibly by attenuating NF-κB.
Keywords: ARE pathway; Anticancer compound; Coumarins; Esculetin; KEAP1; Molecular target; NF-κB; Nrf2; Pancreatic cancer.
Figures
References
-
- Bhanot A, Sharma R, Noolvi MN. Natural sources as potential anti-cancer agents: a review. Int J Phytomedicine. 2011;3:09–26.
-
- Kawaii S, Tomono Y, Ogawa K, Sugiura M, Yano M, Yoshizawa Y. The antiproliferative effect of coumarins on several cancer cell lines. Anticancer Res. 2001;21:917–23. - PubMed
-
- Yue J-M, Xu J, Zhao Y, Sun H-D, Lin Z-W. Chemical components from ceratostigma willmottianum. J Nat Prod. 1997;60:1031–3. doi: 10.1021/np970044u. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

