The association between dietary vitamin A intake and pancreatic cancer risk: a meta-analysis of 11 studies
- PMID: 27756825
- PMCID: PMC5293573
- DOI: 10.1042/BSR20160341
The association between dietary vitamin A intake and pancreatic cancer risk: a meta-analysis of 11 studies
Abstract
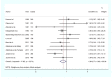
Whether dietary vitamin A intake could reduce pancreatic cancer risk is still conflicting. We therefore conducted a meta-analysis to summarize the evidence from epidemiological studies. We searched the databases of PubMed and Web of Knowledge up to July 2016. Random model was used to combine study-specific relative risks (RR) and 95% confidence interval (CI). Publication bias was assessed by Egger regression asymmetry test and Begg's funnel plot. Eleven studies (10 case-control studies and 1 cohort study) involving 2705 pancreatic cancer cases were included in the present study. The RR (95% CI) of pancreatic cancer for highest category of vitamin A intake compared with lowest category was 0.839 (95% CI=0.712-0.988) with low heterogeneity detected (I2=17.8%, Pheterogeneity=0.274). The relationships were also significant for studies designed by case-control [RR=0.808, 95% CI=0.690-0.947], as well as in European population [RR=0.821, 95% CI=0.693-0.972]. No evidence of publication bias was found. This meta-analysis demonstrated that dietary vitamin A intake might inversely associated with the risk of pancreatic cancer.
Keywords: meta-analysis; pancreatic cancer; vitamin A.
© 2016 The Author(s).
Figures


Similar articles
-
Association between vitamin C intake and the risk of pancreatic cancer: a meta-analysis of observational studies.Sci Rep. 2015 Sep 11;5:13973. doi: 10.1038/srep13973. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26360104 Free PMC article.
-
Cruciferous vegetable consumption and the risk of pancreatic cancer: a meta-analysis.World J Surg Oncol. 2015 Feb 12;13:44. doi: 10.1186/s12957-015-0454-4. World J Surg Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25889229 Free PMC article.
-
Association between selenium intake and the risk of pancreatic cancer: a meta-analysis of observational studies.Biosci Rep. 2016 Oct 14;36(5):e00395. doi: 10.1042/BSR20160345. Print 2016 Oct. Biosci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27623938 Free PMC article.
-
The association between dietary zinc intake and risk of pancreatic cancer: a meta-analysis.Biosci Rep. 2017 Jun 8;37(3):BSR20170155. doi: 10.1042/BSR20170155. Print 2017 Jun 30. Biosci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28428431 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association between Dietary Vitamin A Intake and the Risk of Glioma: Evidence from a Meta-analysis.Nutrients. 2015 Oct 28;7(11):8897-904. doi: 10.3390/nu7115438. Nutrients. 2015. PMID: 26516909 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dietary Factors Associated with Pancreatic Cancer Risk in Minia, Egypt: Principal Component Analysis.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2018 Feb 26;19(2):449-455. doi: 10.22034/APJCP.2018.19.2.449. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2018. PMID: 29480075 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The therapeutic potential of vitamins A, C, and D in pancreatic cancer.Heliyon. 2024 Dec 31;11(1):e41598. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e41598. eCollection 2025 Jan 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39850424 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting Fibrosis: The Bridge That Connects Pancreatitis and Pancreatic Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 7;22(9):4970. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094970. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34067040 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modifiable and Non-Modifiable Risk Factors for the Development of Non-Hereditary Pancreatic Cancer.Medicina (Kaunas). 2022 Jul 22;58(8):978. doi: 10.3390/medicina58080978. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022. PMID: 35893093 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Science-Driven Nutritional Interventions for the Prevention and Treatment of Cancer.Cancer Discov. 2022 Oct 5;12(10):2258-2279. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-22-0504. Cancer Discov. 2022. PMID: 35997502 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Klapman J., Malafa M.P. Early detection of pancreatic cancer: why, who, and how to screen. Cancer Control. 2008;15:280–287. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

