Eriocalyxin B, a natural diterpenoid, inhibited VEGF-induced angiogenesis and diminished angiogenesis-dependent breast tumor growth by suppressing VEGFR-2 signaling
- PMID: 27756875
- PMCID: PMC5347735
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.12652
Eriocalyxin B, a natural diterpenoid, inhibited VEGF-induced angiogenesis and diminished angiogenesis-dependent breast tumor growth by suppressing VEGFR-2 signaling
Abstract
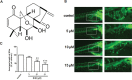
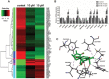
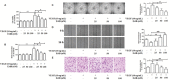
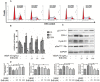
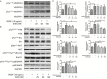
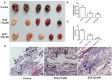
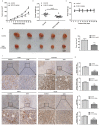
Eriocalyxin B (EriB), a natural ent-kaurane diterpenoid isolated from the plant Isodon eriocalyx var. laxiflora, has emerged as a promising anticancer agent. The effects of EriB on angiogenesis were explored in the present study. Here we demonstrated that the subintestinal vein formation was significantly inhibited by EriB treatment (10, 15 μM) in zebrafish embryos, which was resulted from the alteration of various angiogenic genes as shown in transcriptome profiling. In human umbilical vein endothelial cells, EriB treatment (50, 100 nM) could significantly block vascular endothelial growth factors (VEGF)-induced cell proliferation, tube formation, cell migration and cell invasion. Furthermore, EriB also caused G1 phase cell cycle arrest which was correlated with the down-regulation of the cyclin D1 and CDK4 leading to the inhibition of phosphorylated retinoblastoma protein expression. Investigation of the signal transduction revealed that EriB inhibited VEGF-induced phosphorylation of VEGF receptor-2 via the interaction with the ATP-binding sites according to the molecular docking simulations. The suppression of VEGFR-2 downstream signal transduction cascades was also observed. EriB was showed to inhibit new blood vessel formation in Matrigel plug model and mouse 4T1 breast tumor model. EriB (5 mg/kg/day) treatment was able to decrease tumor vascularization and suppress tumor growth and angiogenesis. Taken together, our findings suggested that EriB is a novel inhibitor of angiogenesis through modulating VEGFR-2 signaling pathway, which could be developed as a promising anti-angiogenic agent for treatment of angiogenesis-related human diseases, such as cancer.
Keywords: Eriocalyxin B; angiogenesis; breast cancer; vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF); vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR-2).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Anti-angiogenic activity and mechanism of kaurane diterpenoids from Wedelia chinensis.Phytomedicine. 2016 Mar 15;23(3):283-92. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2015.12.021. Epub 2016 Jan 29. Phytomedicine. 2016. PMID: 26969382
-
Penduliflaworosin, a Diterpenoid from Croton crassifolius, Exerts Anti-Angiogenic Effect via VEGF Receptor-2 Signaling Pathway.Molecules. 2017 Jan 13;22(1):126. doi: 10.3390/molecules22010126. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28098802 Free PMC article.
-
Antiangiogenic mechanisms of PJ-8, a novel inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling.Carcinogenesis. 2012 May;33(5):1022-30. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgs127. Epub 2012 Mar 20. Carcinogenesis. 2012. PMID: 22436611
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptor system: physiological functions in angiogenesis and pathological roles in various diseases.J Biochem. 2013 Jan;153(1):13-9. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvs136. Epub 2012 Nov 21. J Biochem. 2013. PMID: 23172303 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in tumor angiogenesis and early clinical development of VEGF-receptor kinase inhibitors.Clin Breast Cancer. 2000 Sep;1 Suppl 1:S80-4. doi: 10.3816/cbc.2000.s.015. Clin Breast Cancer. 2000. PMID: 11970755 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanistic Pathways and Molecular Targets of Plant-Derived Anticancer ent-Kaurane Diterpenes.Biomolecules. 2020 Jan 16;10(1):144. doi: 10.3390/biom10010144. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 31963204 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 signaling pathways in cancer angiogenesis, invasion, and metastasis by natural compounds: a comprehensive and critical review.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2024 Mar;43(1):501-574. doi: 10.1007/s10555-023-10136-9. Epub 2023 Oct 4. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2024. PMID: 37792223 Review.
-
Targeting VEGF/VEGFRs Pathway in the Antiangiogenic Treatment of Human Cancers by Traditional Chinese Medicine.Integr Cancer Ther. 2018 Sep;17(3):582-601. doi: 10.1177/1534735418775828. Epub 2018 May 28. Integr Cancer Ther. 2018. PMID: 29807443 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A marine sponge associated fungal metabolite monacolin X suppresses angiogenesis by down regulating VEGFR2 signaling.RSC Adv. 2019 Aug 27;9(46):26646-26667. doi: 10.1039/c9ra05262c. eCollection 2019 Aug 23. RSC Adv. 2019. PMID: 35528587 Free PMC article.
-
Vialinin A, an Edible Mushroom-Derived p-Terphenyl Antioxidant, Prevents VEGF-Induced Neovascularization In Vitro and In Vivo.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018 Feb 6;2018:1052102. doi: 10.1155/2018/1052102. eCollection 2018. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018. PMID: 29541344 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

