Plumbagin protects liver against fulminant hepatic failure and chronic liver fibrosis via inhibiting inflammation and collagen production
- PMID: 27756878
- PMCID: PMC5347738
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.12655
Plumbagin protects liver against fulminant hepatic failure and chronic liver fibrosis via inhibiting inflammation and collagen production
Abstract
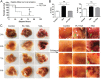
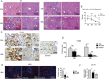
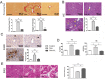
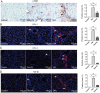
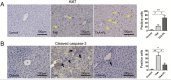
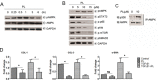
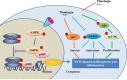
Plumbagin is a quinonoid constituent extracted from Plumbago genus, and it exhibits diverse pharmacological effects. This study thoroughly investigated the effects of plumbagin on thioacetamide-induced acute and chronic liver injury. Results shown that plumbagin increased survival rate, reduced liver congestion and inflammation, and decreased macrophages and neutrophils in the fulminant hepatic failure model, and remarkably diminished liver fibrosis and inflammation in the chronic liver injury model. Furthermore, plumbagin significantly suppress the HSCs/myofibroblasts activation by reduced expression of markers α-SMA and COL-1/3, and reduced macrophage in liver. In the in vitro study, plumbagin induced apoptosis and suppressed the proliferation of LX-2 cells (human HSCs). Plumbagin treatment increased AMPK phosphorylation and attenuated NF-κB, STAT3, and Akt/mTOR signals in LX-2 cells, while SMAD2 phosphorylation was not changed. Noticeably, plumbagin promoted AMPK binding to p300 which is a cofactor of SMAD complex, this may further competitively decreases the p300/SMAD complex initiated transcription of COL-1/3 and α-SMA. Additionally, plumbagin hampered inflammation related NF-κB signal in RAW 264.7 cells. In conclusion, these findings indicate that plumbagin may be a powerful drug candidate to protect the liver from acute and chronic damage by inhibiting inflammation and collagen production.
Keywords: fulminant hepatic failure; hepatic stellate cell; inflammation; liver fibrosis; plumbagin.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing financial interests: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Guggulsterone attenuates activation and survival of hepatic stellate cell by inhibiting nuclear factor kappa B activation and inducing apoptosis.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013 Dec;28(12):1859-68. doi: 10.1111/jgh.12314. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013. PMID: 23808824
-
Antifibrotic effects of luteolin on hepatic stellate cells and liver fibrosis by targeting AKT/mTOR/p70S6K and TGFβ/Smad signalling pathways.Liver Int. 2015 Apr;35(4):1222-33. doi: 10.1111/liv.12638. Epub 2014 Aug 5. Liver Int. 2015. PMID: 25040634
-
Ferulic acid attenuates liver fibrosis and hepatic stellate cell activation via inhibition of TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018 Dec 3;12:4107-4115. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S186726. eCollection 2018. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018. PMID: 30584275 Free PMC article.
-
Anticancer Properties and Pharmaceutical Applications of Plumbagin: A Review.Am J Chin Med. 2017;45(3):423-441. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X17500264. Epub 2017 Mar 30. Am J Chin Med. 2017. PMID: 28359198 Review.
-
Hepatic fibrosis: It is time to go with hepatic stellate cell-specific therapeutic targets.Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2018 Jun;17(3):192-197. doi: 10.1016/j.hbpd.2018.04.003. Epub 2018 Apr 21. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2018. PMID: 29709350 Review.
Cited by
-
Anti-Obesity Effects of Dietary Fibers Extracted from Flaxseed Cake in Diet-Induced Obese Mice.Nutrients. 2023 Mar 31;15(7):1718. doi: 10.3390/nu15071718. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37049557 Free PMC article.
-
Plumbagin attenuates Bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis in mice.Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2022 Oct 21;18(1):93. doi: 10.1186/s13223-022-00734-7. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36271442 Free PMC article.
-
Ethanol Extract of Licorice Alleviates HFD-Induced Liver Fat Accumulation in Association with Modulation of Gut Microbiota and Intestinal Metabolites in Obesity Mice.Nutrients. 2022 Oct 8;14(19):4180. doi: 10.3390/nu14194180. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36235833 Free PMC article.
-
The Ameliorative Effects of Fucoidan in Thioacetaide-Induced Liver Injury in Mice.Molecules. 2021 Mar 30;26(7):1937. doi: 10.3390/molecules26071937. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33808318 Free PMC article.
-
Plumbagin attenuates traumatic tracheal stenosis in rats and inhibits lung fibroblast proliferation and differentiation via TGF-β1/Smad and Akt/mTOR pathways.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(1):4475-4488. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1954580. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34304701 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wallace K, Burt A, Wright M. Liver fibrosis. Biochem J. 2008;411:1–18. - PubMed
-
- Bernal W, Auzinger G, Dhawan A, Wendon J. Acute liver failure. The Lancet. 2010;376:190–201. - PubMed
-
- Wallace K, Burt AD, Wright MC. Liver fibrosis. Biochemical Journal. 2008;411:1–18. - PubMed
-
- Parimala R, Sachdanandam P. Effect of Plumbagin on some glucose metabolising enzymes studied in rats in experimental hepatoma. Molecular and cellular biochemistry. 1993;125:59–63. - PubMed
-
- Sharma I, Gusain D, Dixit VP. Hypolipidaemic and antiatherosclerotic effects of plumbagin in rabbits. Indian journal of physiology and pharmacology. 1991;35:10–14. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

