MPP2 is a postsynaptic MAGUK scaffold protein that links SynCAM1 cell adhesion molecules to core components of the postsynaptic density
- PMID: 27756895
- PMCID: PMC5069480
- DOI: 10.1038/srep35283
MPP2 is a postsynaptic MAGUK scaffold protein that links SynCAM1 cell adhesion molecules to core components of the postsynaptic density
Abstract
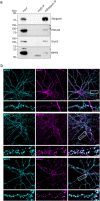
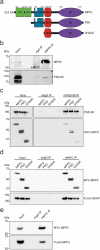
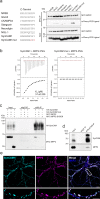
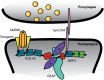
At neuronal synapses, multiprotein complexes of trans-synaptic adhesion molecules, scaffold proteins and neurotransmitter receptors assemble to essential building blocks required for synapse formation and maintenance. Here we describe a novel role for the membrane-associated guanylate kinase (MAGUK) protein MPP2 (MAGUK p55 subfamily member 2) at synapses of rat central neurons. Through interactions mediated by its C-terminal SH3-GK domain module, MPP2 binds to the abundant postsynaptic scaffold proteins PSD-95 and GKAP and localises to postsynaptic sites in hippocampal neurons. MPP2 also colocalises with the synaptic adhesion molecule SynCAM1. We demonstrate that the SynCAM1 C-terminus interacts directly with the MPP2 PDZ domain and that MPP2 does not interact in this manner with other highly abundant postsynaptic transmembrane proteins. Our results highlight a previously unexplored role for MPP2 at postsynaptic sites as a scaffold that links SynCAM1 cell adhesion molecules to core proteins of the postsynaptic density.
Figures
Similar articles
-
GKAP, a novel synaptic protein that interacts with the guanylate kinase-like domain of the PSD-95/SAP90 family of channel clustering molecules.J Cell Biol. 1997 Feb 10;136(3):669-78. doi: 10.1083/jcb.136.3.669. J Cell Biol. 1997. PMID: 9024696 Free PMC article.
-
A functional role of postsynaptic density-95-guanylate kinase-associated protein complex in regulating Shank assembly and stability to synapses.J Neurosci. 2004 Oct 20;24(42):9391-404. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3314-04.2004. J Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15496675 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of guanylate kinase-associated protein, a postsynaptic density protein at excitatory synapses that interacts directly with postsynaptic density-95/synapse-associated protein 90.J Neurosci. 1997 Aug 1;17(15):5687-96. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.17-15-05687.1997. J Neurosci. 1997. PMID: 9221768 Free PMC article.
-
[Scaffold proteins (MAGUK, Shank and Homer) in postsynaptic density in the central nervous system].Postepy Biochem. 2007;53(2):188-97. Postepy Biochem. 2007. PMID: 17969881 Review. Polish.
-
MAGUKs, synaptic development, and synaptic plasticity.Neuroscientist. 2011 Oct;17(5):493-512. doi: 10.1177/1073858410386384. Epub 2011 Apr 15. Neuroscientist. 2011. PMID: 21498811 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Involvement of membrane palmitoylated protein 2 (MPP2) in the synaptic molecular complex at the mouse cerebellar glomerulus.Histochem Cell Biol. 2022 Nov;158(5):497-511. doi: 10.1007/s00418-022-02137-6. Epub 2022 Jul 19. Histochem Cell Biol. 2022. PMID: 35854144
-
Demethylation of miR-34a upregulates expression of membrane palmitoylated proteins and promotes the apoptosis of liver cancer cells.World J Gastroenterol. 2021 Feb 14;27(6):470-486. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i6.470. World J Gastroenterol. 2021. PMID: 33642822 Free PMC article.
-
Global RNA editome landscape discovers reduced RNA editing in glioma: loss of editing of gamma-amino butyric acid receptor alpha subunit 3 (GABRA3) favors glioma migration and invasion.PeerJ. 2020 Sep 29;8:e9755. doi: 10.7717/peerj.9755. eCollection 2020. PeerJ. 2020. PMID: 33062411 Free PMC article.
-
stAPAminer: Mining Spatial Patterns of Alternative Polyadenylation for Spatially Resolved Transcriptomic Studies.Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2023 Jun;21(3):601-618. doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2023.01.003. Epub 2023 Jan 18. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2023. PMID: 36669641 Free PMC article.
-
Differential Contribution of Cadm1-Cadm3 Cell Adhesion Molecules to Peripheral Myelinated Axons.J Neurosci. 2021 Feb 17;41(7):1393-1400. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2736-20.2020. Epub 2021 Jan 4. J Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33397712 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

