Gene-expression reversal of lncRNAs and associated mRNAs expression in active vs latent HIV infection
- PMID: 27756902
- PMCID: PMC5069461
- DOI: 10.1038/srep34862
Gene-expression reversal of lncRNAs and associated mRNAs expression in active vs latent HIV infection
Abstract
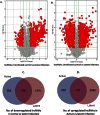
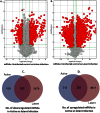
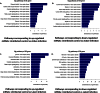
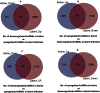
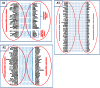
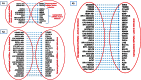
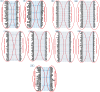
Interplay between lncRNAs and mRNAs is rapidly emerging as a key epigenetic mechanism in controlling various cell functions. HIV can actively infect and/or can persist latently for years by manipulating host epigenetics; however, its molecular essence remains undiscovered in entirety. Here for the first time, we delineate the influence of HIV on global lncRNAs expression in monocytic cells lines. Our analysis revealed the expression modulation of nearly 1060 such lncRNAs which are associated with differentially expressed mRNAs in active and latent infection. This suggests a greater role of lncRNAs in regulating transcriptional and post-transcriptional gene expression during HIV infection. The differentially expressed mRNAs were involved in several different biological pathways where immunological networks were most enriched. Importantly, we discovered that HIV induces expression reversal of more than 150 lncRNAs between its active and latent infection. Also, hundreds of unique lncRNAs were identified in both infection conditions. The pathology specific "gene-expression reversal" and "on-and-off" switching of lncRNAs and associated mRNAs may lead to establish the relationship between active and HIV infection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

References
-
- Chun T. W. & Fauci A. S. HIV reservoirs: pathogenesis and obstacles to viral eradication and cure. AIDS 26, 1261–1268 (2012). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

