Evaluation of effects of melatonin and caffeic acid phenethyl ester on acute potassium dichromate toxicity and genotoxicity in rats
- PMID: 27756952
- PMCID: PMC4980929
- DOI: 10.4103/0253-7613.186213
Evaluation of effects of melatonin and caffeic acid phenethyl ester on acute potassium dichromate toxicity and genotoxicity in rats
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this study is to investigate the possible protective effects of melatonin and caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE) on potassium dichromate (K2 Cr2O7)-induced nephrotoxicity and genotoxicity.
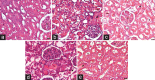
Methods: A total of 40 Wistar albino rats were divided into five groups: control, K2Cr2O7(K2Cr2O715 mg/kg, one dose, i.p.), K2Cr2O7 + melatonin, K2Cr2O7 + CAPE, and K2Cr2O7 + melatonin + CAPE. Urine and blood samples were collected from rats before scarification. One kidney was collected for histopathological studies, and the other was stored at -80°C for further determination of catalase (CAT), superoxide dismutase (SOD), malondialdehyde (MDA), glutathione (GSH), glutathione S-transferase (GST), and glutathione reductase (GR) levels with spectrophotometric method. Comet assay was used to evaluate the genotoxicity.
Results: We observed a significant amelioration in genotoxicity by melatonin and simultaneous melatonin + CAPE treatment compared to K2Cr2O7 group (p1, p2< 0.05). SOD, CAT, GSH, GST, and MDA levels did not change when compared with controls. When K2Cr2O7 applied group was treated with melatonin and CAPE, neither melatonin nor CAPE made any changes in kidney GSH, GST, SOD, and MDA levels (P > 0.05). We noted that treatment with CAPE and melatonin + CAPE together caused a significant decrease in renal tissue damage, an upregulation in the kidney CAT levels (P < 0.05) and a slight healing at GR levels when compared with the K2Cr2O7 group.
Conclusion: Our results revealed, CAPE and melatonin may have protective effects on K2Cr2O7 induced nephrotoxicity and cellular damage in rats.
Keywords: Caffeic acid phenethyl ester; melatonin; nephrotoxicity; oxidative stress; potassium dichromate.
Figures

References
-
- Crump C, Crump K, Hack E, Luippold R, Mundt K, Liebig E, et al. Dose-response and risk assessment of airborne hexavalent chromium and lung cancer mortality. Risk Anal. 2003;23:1147–63. - PubMed
-
- Fatima S, Mahmood R. Vitamin C attenuates potassium dichromate-induced nephrotoxicity and alterations in renal brush border membrane enzymes and phosphate transport in rats. Clin Chim Acta. 2007;386:94–9. - PubMed
-
- Susa N, Ueno S, Furukawa Y, Ueda J, Sugiyama M. Potent protective effect of melatonin on chromium (VI)-induced DNA single-strand breaks, cytotoxicity, and lipid peroxidation in primary cultures of rat hepatocytes. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1997;144:377–84. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

