Diverse Functions of Small RNAs in Different Plant-Pathogen Communications
- PMID: 27757103
- PMCID: PMC5048074
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.01552
Diverse Functions of Small RNAs in Different Plant-Pathogen Communications
Abstract
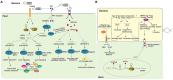
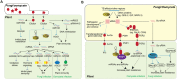
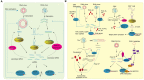
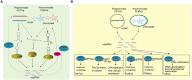
RNA silencing is a conserved mechanism that utilizes small RNAs (sRNAs) to direct the regulation of gene expression at the transcriptional or post-transcriptional level. Plants utilizing RNA silencing machinery to defend pathogen infection was first identified in plant-virus interaction and later was observed in distinct plant-pathogen interactions. RNA silencing is not only responsible for suppressing RNA accumulation and movement of virus and viroid, but also facilitates plant immune responses against bacterial, oomycete, and fungal infection. Interestingly, even the same plant sRNA can perform different roles when encounters with different pathogens. On the other side, pathogens counteract by generating sRNAs that directly regulate pathogen gene expression to increase virulence or target host genes to facilitate pathogen infection. Here, we summarize the current knowledge of the characterization and biogenesis of host- and pathogen-derived sRNAs, as well as the different RNA silencing machineries that plants utilize to defend against different pathogens. The functions of these sRNAs in defense and counter-defense and their mechanisms for regulation during different plant-pathogen interactions are also discussed.
Keywords: RNA silencing; pathogen virulence; plant immunity; plant–pathogen interaction; small RNA.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The function of small RNAs in plant biotic stress response.J Integr Plant Biol. 2016 Apr;58(4):312-27. doi: 10.1111/jipb.12463. Epub 2016 Feb 23. J Integr Plant Biol. 2016. PMID: 26748943 Review.
-
Small RNA Regulators of Plant-Hemipteran Interactions: Micromanagers with Versatile Roles.Front Plant Sci. 2016 Aug 30;7:1241. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.01241. eCollection 2016. Front Plant Sci. 2016. PMID: 27625654 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Small RNAs--the secret agents in the plant-pathogen interactions.Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2015 Aug;26:87-94. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2015.05.033. Epub 2015 Jun 26. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2015. PMID: 26123395 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Small RNAs in plant defense responses during viral and bacterial interactions: similarities and differences.Front Plant Sci. 2013 Sep 5;4:343. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2013.00343. Front Plant Sci. 2013. PMID: 24046772 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Small Talk: On the Possible Role of Trans-Kingdom Small RNAs during Plant-Virus-Vector Tritrophic Communication.Plants (Basel). 2023 Mar 22;12(6):1411. doi: 10.3390/plants12061411. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36987098 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Small RNA-based plant protection against diseases.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Aug 18;13:951097. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.951097. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36061762 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rice stripe virus-derived siRNAs play different regulatory roles in rice and in the insect vector Laodelphax striatellus.BMC Plant Biol. 2018 Oct 4;18(1):219. doi: 10.1186/s12870-018-1438-7. BMC Plant Biol. 2018. PMID: 30286719 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-Mediated Gene Silencing in Plant Defense and Viral Counter-Defense.Front Microbiol. 2017 Sep 20;8:1801. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01801. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28979248 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Early changes in microRNA expression in Arabidopsis plants infected with the fungal pathogen Fusarium graminearum.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Aug 10:2024.05.29.596347. doi: 10.1101/2024.05.29.596347. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: PLoS One. 2025 Feb 06;20(2):e0318532. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0318532. PMID: 39149262 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Regulation of plant biotic interactions and abiotic stress responses by inositol polyphosphates.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Aug 11;13:944515. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.944515. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36035672 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adkar-Purushothama C. R., Brosseau C., Giguere T., Sano T., Moffett P., Perreault J. P. (2015). Small RNA derived from the virulence modulating region of the potato spindle tuber viroid silences callose synthase genes of tomato plants. Plant Cell 27 2178–2194. 10.1105/tpc.15.00523 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Avina-Padilla K., Martinez de la Vega O., Rivera-Bustamante R., Martinez-Soriano J. P., Owens R. A., Hammond R. W., et al. (2015). In silico prediction and validation of potential gene targets for pospiviroid-derived small RNAs during tomato infection. Gene 564 197–205. 10.1016/j.gene.2015.03.076 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

