Quality of Life and Aesthetic Plastic Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
- PMID: 27757327
- PMCID: PMC5054993
- DOI: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000000833
Quality of Life and Aesthetic Plastic Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Abstract
Quality of life (QoL) is an important outcome in plastic surgery. However, authors use different scales to address this subject, making it difficult to compare the outcomes. To address this discrepancy, the aim of this study was to perform a systematic review and a random effect meta-analysis.
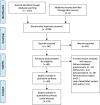
Methods: The search was made in two electronic databases (LILACS and PUBMED) using Mesh and non-Mesh terms related to aesthetic plastic surgery and QoL. We performed qualitative and quantitative analyses of the gathered data. We calculated a random effect meta-analysis with Der Simonian and Laird as variance estimator to compare pre- and postoperative QoL standardized mean difference. To check if there is difference between aesthetic surgeries, we compared reduction mammoplasty to other aesthetic surgeries.
Results: Of 1,715 identified, 20 studies were included in the qualitative analysis and 16 went through quantitative analysis. The random effect of all aesthetic surgeries shows that QoL improved after surgery. Reduction mammoplasty has improved QoL more than other procedures in social functioning and physical functioning domains.
Conclusions: Aesthetic plastic surgery increases QoL. Reduction mammoplasty seems to have better improvement compared with other aesthetic surgeries.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Dreher received a governmental fund (CAPES) as a postgraduate Master of Science Degree student. None of the other authors have any financial disclosures. The Article Processing Charge was paid for by the authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sacroiliac Joint Fusion Methodology - Minimally Invasive Compared to Screw-Type Surgeries: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Pain Physician. 2019 Jan;22(1):29-40. Pain Physician. 2019. PMID: 30700066
-
Quality of life outcomes in patients undergoing facial gender affirming surgery: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Int J Transgend Health. 2023 Nov 20;25(4):653-662. doi: 10.1080/26895269.2023.2278736. eCollection 2024. Int J Transgend Health. 2023. PMID: 39465064 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A systematic review of patient reported outcome measures for women with macromastia who have undergone breast reduction surgery.Gland Surg. 2019 Aug;8(4):431-440. doi: 10.21037/gs.2019.03.08. Gland Surg. 2019. PMID: 31538069 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reduction Mammoplasty: A Comparison Between Operations Performed by Plastic Surgery and General Surgery.Eplasty. 2015 Sep 22;15:e41. eCollection 2015. Eplasty. 2015. PMID: 26435766 Free PMC article.
-
A Procedure and Complication-Specific Assessment of Smoking in Aesthetic Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Plast Surg (Oakv). 2024 Feb;32(1):115-126. doi: 10.1177/22925503221085083. Epub 2022 Mar 18. Plast Surg (Oakv). 2024. PMID: 38433792 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Invited Discussion on: Quality of Life and Concurrent Procedures in Truncal Body Contouring Patients: A Single-Center Retrospective Study.Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2021 Aug;45(4):1628-1632. doi: 10.1007/s00266-021-02192-9. Epub 2021 Mar 10. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2021. PMID: 33693982 No abstract available.
-
The impact on quality-of-life following treatment of surgical facial scars with laser-based therapy: a scoping review.Arch Dermatol Res. 2023 Dec 16;316(1):47. doi: 10.1007/s00403-023-02779-z. Arch Dermatol Res. 2023. PMID: 38103110
-
The Crooked Nose-Surgical Algorithm in Post-Traumatic Patient-Evaluation of Surgical Sequence.J Clin Med. 2024 Dec 27;14(1):87. doi: 10.3390/jcm14010087. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39797171 Free PMC article.
-
Surgery beyond bodies: Soul surgery and social surgery.Front Surg. 2022 Sep 7;9:950172. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2022.950172. eCollection 2022. Front Surg. 2022. PMID: 36157420 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Polish Translation and Linguistic Validation of the SCAR-Q.Cureus. 2024 Jan 24;16(1):e52848. doi: 10.7759/cureus.52848. eCollection 2024 Jan. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38406147 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cano SJ, Klassen A, Pusic AL. The science behind quality-of-life measurement: a primer for plastic surgeons. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2009;123:98e–106e. - PubMed
-
- Thoma A, Ignacy TA, Duku EK, et al. Randomized controlled trial comparing health-related quality of life in patients undergoing vertical scar versus inverted T-shaped reduction mammaplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2013;132:48e–60e. - PubMed
-
- Litner JA, Rotenberg BW, Dennis M, et al. Impact of cosmetic facial surgery on satisfaction with appearance and quality of life. Arch Facial Plast Surg. 2008;10:79–83. - PubMed
-
- Coriddi MR, Koltz PF, Chen R, et al. Changes in quality of life and functional status following abdominal contouring in the massive weight loss population. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2011;128:520–526. - PubMed
-
- Klassen A, Jenkinson C, Fitzpatrick R, et al. Patients’ health related quality of life before and after aesthetic surgery. Br J Plast Surg. 1996;49:433–438. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources