Promiscuous targeting of bromodomains by bromosporine identifies BET proteins as master regulators of primary transcription response in leukemia
- PMID: 27757418
- PMCID: PMC5061470
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.1600760
Promiscuous targeting of bromodomains by bromosporine identifies BET proteins as master regulators of primary transcription response in leukemia
Abstract
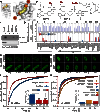
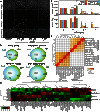
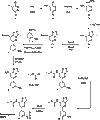
Bromodomains (BRDs) have emerged as compelling targets for cancer therapy. The development of selective and potent BET (bromo and extra-terminal) inhibitors and their significant activity in diverse tumor models have rapidly translated into clinical studies and have motivated drug development efforts targeting non-BET BRDs. However, the complex multidomain/subunit architecture of BRD protein complexes complicates predictions of the consequences of their pharmacological targeting. To address this issue, we developed a promiscuous BRD inhibitor [bromosporine (BSP)] that broadly targets BRDs (including BETs) with nanomolar affinity, creating a tool for the identification of cellular processes and diseases where BRDs have a regulatory function. As a proof of principle, we studied the effects of BSP on leukemic cell lines known to be sensitive to BET inhibition and found, as expected, strong antiproliferative activity. Comparison of the modulation of transcriptional profiles by BSP after a short exposure to the inhibitor resulted in a BET inhibitor signature but no significant additional changes in transcription that could account for inhibition of other BRDs. Thus, nonselective targeting of BRDs identified BETs, but not other BRDs, as master regulators of context-dependent primary transcription response.
Keywords: BET; Bromodomains; epigenetics; inhibition; leukemias.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Interactome Rewiring Following Pharmacological Targeting of BET Bromodomains.Mol Cell. 2019 Feb 7;73(3):621-638.e17. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2018.11.006. Epub 2018 Dec 13. Mol Cell. 2019. PMID: 30554943 Free PMC article.
-
BET bromodomain inhibitors in leukemia.Exp Hematol. 2015 Aug;43(8):718-31. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2015.06.004. Epub 2015 Jul 9. Exp Hematol. 2015. PMID: 26163798 Review.
-
PFI-1, a highly selective protein interaction inhibitor, targeting BET Bromodomains.Cancer Res. 2013 Jun 1;73(11):3336-46. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-3292. Epub 2013 Apr 10. Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23576556 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of BET bromodomains as a therapeutic strategy for cancer drug discovery.Oncotarget. 2015 Mar 20;6(8):5501-16. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3551. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25849938 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Selective inhibition of the BD2 bromodomain of BET proteins in prostate cancer.Nature. 2020 Feb;578(7794):306-310. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-1930-8. Epub 2020 Jan 22. Nature. 2020. PMID: 31969702
Cited by
-
BET bromodomain inhibitors PFI-1 and JQ1 are identified in an epigenetic compound screen to enhance C9ORF72 gene expression and shown to ameliorate C9ORF72-associated pathological and behavioral abnormalities in a C9ALS/FTD model.Clin Epigenetics. 2021 Mar 16;13(1):56. doi: 10.1186/s13148-021-01039-z. Clin Epigenetics. 2021. PMID: 33726839 Free PMC article.
-
A chemical toolbox for the study of bromodomains and epigenetic signaling.Nat Commun. 2019 Apr 23;10(1):1915. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-09672-2. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31015424 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic modulation through BET bromodomain inhibitors as a novel therapeutic strategy for progranulin-deficient frontotemporal dementia.Sci Rep. 2024 Apr 20;14(1):9064. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-59110-7. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38643236 Free PMC article.
-
Multiplexed Small-Molecule-Ligand Binding Assays by Affinity Labeling and DNA Sequence Analysis.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2022 Jan 17;61(3):e202113515. doi: 10.1002/anie.202113515. Epub 2021 Dec 3. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2022. PMID: 34758183 Free PMC article.
-
An Activity-Based Probe Targeting Non-Catalytic, Highly Conserved Amino Acid Residues within Bromodomains.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2019 Jan 21;58(4):1007-1012. doi: 10.1002/anie.201807825. Epub 2018 Dec 27. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2019. PMID: 30589164 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Filippakopoulos P., Picaud S., Mangos M., Keates T., Lambert J.-P., Barsyte-Lovejoy D., Felletar I., Volkmer R., Müller S., Pawson T., Gingras A.-C., Arrowsmith C. H., Knapp S., Histone recognition and large-scale structural analysis of the human bromodomain family. Cell 149, 214–231 (2012). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Filippakopoulos P., Knapp S., Targeting bromodomains: Epigenetic readers of lysine acetylation. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 13, 337–356 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Filippakopoulos P., Qi J., Picaud S., Shen Y., Smith W. B., Fedorov O., Morse E. M., Keates T., Hickman T. T., Felletar I., Philpott M., Munro S., McKeown M. R., Wang Y., Christie A. L., West N., Cameron M. J., Schwartz B., Heightman T. D., La Thangue N., French C. A., Wiest O., Kung A. L., Knapp S., Bradner J. E., Selective inhibition of BET bromodomains. Nature 468, 1067–1073 (2010). - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

