Can intraoperative neurophysiologic monitoring during cervical spine decompression predict post-operative segmental C5 palsy?
- PMID: 27757428
- PMCID: PMC5067277
- DOI: 10.21037/jss.2016.09.09
Can intraoperative neurophysiologic monitoring during cervical spine decompression predict post-operative segmental C5 palsy?
Abstract
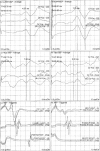
Background: C5 nerve root palsy is a known complication after cervical laminectomy or laminoplasty, characterized by weakness of the deltoid and bicep brachii muscles. The efficacy of intraoperative monitoring of these muscles is currently unclear. In the current prospective study, intraoperative monitoring through somatosensory (SSEPs), motor (TcMEPs) evoked potentials and real-time electromyography activity (EMG) were analyzed for their ability to detect or prevent deltoid muscle weakness after surgery.
Methods: One hundred consecutive patients undergoing laminectomy/laminoplasty with or without fusion were enrolled. Intraoperative SSEPs, TcMEPs and EMGs from each patient were studied and analyzed.
Results: Intraoperative EMG activity of the C5 nerve root was detected in 34 cases, 10 of which demonstrated a sustained and repetitive EMG activity lasting 5 or more minutes. Paresis of the unilateral deltoid muscle developed in 5 patients, all from the group with sustained C5 EMG activity. None of the patients with weakness of deltoid muscle after surgery demonstrated any abnormal change in TcMEP or SSEP.
Conclusions: Real-time EMG recordings were sensitive to C5 nerve root irritation, whilst SSEPs and TcMEPs were not. Sustained EMG activity of the C5 nerve root during surgery is a possible warning sign of irritation or injury to the nerve.
Keywords: C5 nerve root pasly; Spinal cord monitoring; cervical decompression.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Tanaka N, Nakanishi K, Fujiwara Y, et al. Postoperative segmental C5 palsy after cervical laminoplasty may occur without intraoperative nerve injury: a prospective study with transcranial electric motor-evoked potentials. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2006;31:3013-7. 10.1097/01.brs.0000250303.17840.96 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
