Quantitative Identification of Compound-Dependent On-Modules and Differential Allosteric Modules From Homologous Ischemic Networks
- PMID: 27758049
- PMCID: PMC5080653
- DOI: 10.1002/psp4.12127
Quantitative Identification of Compound-Dependent On-Modules and Differential Allosteric Modules From Homologous Ischemic Networks
Abstract
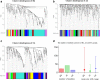
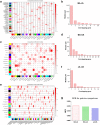
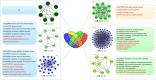
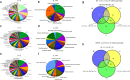
Module-based methods have made much progress in deconstructing biological networks. However, it is a great challenge to quantitatively compare the topological structural variations of modules (allosteric modules [AMs]) under different situations. A total of 23, 42, and 15 coexpression modules were identified in baicalin (BA), jasminoidin (JA), and ursodeoxycholic acid (UA) in a global anti-ischemic mice network, respectively. Then, we integrated the methods of module-based consensus ratio (MCR) and modified Zsummary module statistic to validate 12 BA, 22 JA, and 8 UA on-modules based on comparing with vehicle. The MCRs for pairwise comparisons were 1.55% (BA vs. JA), 1.45% (BA vs. UA), and 1.27% (JA vs. UA), respectively. Five conserved allosteric modules (CAMs) and 17 unique allosteric modules (UAMs) were identified among these groups. In conclusion, module-centric analysis may provide us a unique approach to understand multiple pharmacological mechanisms associated with differential phenotypes in the era of modular pharmacology.
© 2016 The Authors CPT: Pharmacometrics & Systems Pharmacology published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of American Society for Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics.
Figures

References
-
- Xiong, M. , Li, B. , Zhu, Q. , Wang, Y.X. & Zhang, H.Y. Identification of transcription factors for drug‐associated gene modules and biomedical implications. Bioinformatics 30, 305–309 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Wang, Z. , Liu, J. , Yu, Y. , Chen, Y. & Wang, Y. Modular pharmacology: the next paradigm in drug discovery. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 7, 667–677 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Wang, Z. & Wang, Y.Y. Modular pharmacology: deciphering the interacting structural organization of the targeted networks. Drug Discov. Today 18, 560–566 (2013). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

