Bromocriptine and insulin sensitivity in lean and obese subjects
- PMID: 27758845
- PMCID: PMC5097144
- DOI: 10.1530/EC-16-0051
Bromocriptine and insulin sensitivity in lean and obese subjects
Abstract
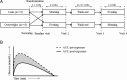
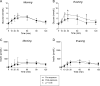
Bromocriptine is a glucose-lowering drug, which was shown to be effective in obese subjects with insulin resistance. It is usually administered in the morning. The exact working mechanism of bromocriptine still has to be elucidated. Therefore, in this open-label randomized prospective cross-over mechanistic study, we assessed whether the timing of bromocriptine administration (morning vs evening) results in different effects and whether these effects differ between lean and obese subjects. We studied the effect of bromocriptine on insulin sensitivity in 8 lean and 8 overweight subjects using an oral glucose tolerance test. The subjects used bromocriptine in randomized cross-over order for 2 weeks in the morning and 2 weeks in the evening. We found that in lean subjects, bromocriptine administration in the evening resulted in a significantly higher post-prandial insulin sensitivity as compared with the pre-exposure visit (glucose area under the curve (AUC) 742 mmol/L * 120 min (695-818) vs 641 (504-750), P = 0.036, AUC for insulin did not change, P = 0.575). In obese subjects, both morning and evening administration of bromocriptine resulted in a significantly higher insulin sensitivity: morning administration in obese: insulin AUC (55,900 mmol/L * 120 min (43,236-96,831) vs 36,448 (25,213-57,711), P = 0.012) and glucose AUC P = 0.069; evening administration in obese: glucose AUC (735 mmol/L * 120 min (614-988) vs 644 (568-829), P = 0.017) and insulin AUC, P = 0.208. In conclusion, bromocriptine increases insulin sensitivity in both lean and obese subjects. In lean subjects, this effect only occurred when bromocriptine was administrated in the evening, whereas in the obese, insulin sensitivity increased independent of the timing of bromocriptine administration.
Keywords: bromocriptine; circadian rhythm; dopamine; insulin sensitivity; obesity.
© 2016 The authors.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effects of oral L-carnitine supplementation on insulin sensitivity indices in response to glucose feeding in lean and overweight/obese males.Amino Acids. 2011 Jul;41(2):507-15. doi: 10.1007/s00726-010-0770-5. Epub 2010 Oct 21. Amino Acids. 2011. PMID: 20963457
-
Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of insulin glargine given in the evening as compared with in the morning in type 2 diabetes.Diabetes Care. 2015 Mar;38(3):503-12. doi: 10.2337/dc14-0649. Epub 2014 Dec 18. Diabetes Care. 2015. PMID: 25524950 Clinical Trial.
-
Fasting and daylong triglycerides in obesity with and without type 2 diabetes.Metabolism. 2003 Aug;52(8):1043-9. doi: 10.1016/s0026-0495(03)00106-9. Metabolism. 2003. PMID: 12898471 Clinical Trial.
-
Day-night differences in the kinetics and dynamics of insulin: diabetic versus normal Yucatan minipigs.Chronobiol Int. 1996 Aug;13(3):213-25. doi: 10.3109/07420529609012654. Chronobiol Int. 1996. PMID: 8874984
-
Evening versus morning injections of growth hormone (GH) in GH-deficient patients: effects on 24-hour patterns of circulating hormones and metabolites.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1990 Jan;70(1):207-14. doi: 10.1210/jcem-70-1-207. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1990. PMID: 2294131 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Integrative metagenomic and metabolomic analyses reveal gut microbiota-derived multiple hits connected to development of gestational diabetes mellitus in humans.Gut Microbes. 2023 Jan-Dec;15(1):2154552. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2022.2154552. Gut Microbes. 2023. PMID: 36550785 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of Dopamine on Insulin Secretion in Healthy Controls.Indian J Crit Care Med. 2018 Apr;22(4):209-213. doi: 10.4103/ijccm.IJCCM_175_17. Indian J Crit Care Med. 2018. PMID: 29743758 Free PMC article.
-
Bromocriptine-QR Therapy Reduces Sympathetic Tone and Ameliorates a Pro-Oxidative/Pro-Inflammatory Phenotype in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells and Plasma of Type 2 Diabetes Subjects.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 9;23(16):8851. doi: 10.3390/ijms23168851. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36012132 Free PMC article.
-
Brain Dopamine-Clock Interactions Regulate Cardiometabolic Physiology: Mechanisms of the Observed Cardioprotective Effects of Circadian-Timed Bromocriptine-QR Therapy in Type 2 Diabetes Subjects.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 26;24(17):13255. doi: 10.3390/ijms241713255. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37686060 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Time-of-Day-Dependent Effects of Bromocriptine to Ameliorate Vascular Pathology and Metabolic Syndrome in SHR Rats Held on High Fat Diet.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 7;22(11):6142. doi: 10.3390/ijms22116142. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34200262 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

