Chromosome conformation elucidates regulatory relationships in developing human brain
- PMID: 27760116
- PMCID: PMC5358922
- DOI: 10.1038/nature19847
Chromosome conformation elucidates regulatory relationships in developing human brain
Abstract
Three-dimensional physical interactions within chromosomes dynamically regulate gene expression in a tissue-specific manner. However, the 3D organization of chromosomes during human brain development and its role in regulating gene networks dysregulated in neurodevelopmental disorders, such as autism or schizophrenia, are unknown. Here we generate high-resolution 3D maps of chromatin contacts during human corticogenesis, permitting large-scale annotation of previously uncharacterized regulatory relationships relevant to the evolution of human cognition and disease. Our analyses identify hundreds of genes that physically interact with enhancers gained on the human lineage, many of which are under purifying selection and associated with human cognitive function. We integrate chromatin contacts with non-coding variants identified in schizophrenia genome-wide association studies (GWAS), highlighting multiple candidate schizophrenia risk genes and pathways, including transcription factors involved in neurogenesis, and cholinergic signalling molecules, several of which are supported by independent expression quantitative trait loci and gene expression analyses. Genome editing in human neural progenitors suggests that one of these distal schizophrenia GWAS loci regulates FOXG1 expression, supporting its potential role as a schizophrenia risk gene. This work provides a framework for understanding the effect of non-coding regulatory elements on human brain development and the evolution of cognition, and highlights novel mechanisms underlying neuropsychiatric disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests. Readers are welcome to comment on the online version of the paper.
Figures








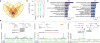
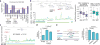
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 MH094714/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K99 MH102357/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- T32 MH073526/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES024995/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH101782/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH100027/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH105991/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH110927/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R37 MH060233/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI028697/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R00 MH102357/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH060233/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH103339/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES022282/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- F30 MH099886/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

