Alignment of Homologous Chromosomes and Effective Repair of Programmed DNA Double-Strand Breaks during Mouse Meiosis Require the Minichromosome Maintenance Domain Containing 2 (MCMDC2) Protein
- PMID: 27760146
- PMCID: PMC5070785
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006393
Alignment of Homologous Chromosomes and Effective Repair of Programmed DNA Double-Strand Breaks during Mouse Meiosis Require the Minichromosome Maintenance Domain Containing 2 (MCMDC2) Protein
Abstract
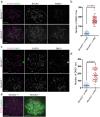
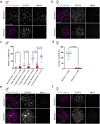
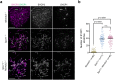
Orderly chromosome segregation during the first meiotic division requires meiotic recombination to form crossovers between homologous chromosomes (homologues). Members of the minichromosome maintenance (MCM) helicase family have been implicated in meiotic recombination. In addition, they have roles in initiation of DNA replication, DNA mismatch repair and mitotic DNA double-strand break repair. Here, we addressed the function of MCMDC2, an atypical yet conserved MCM protein, whose function in vertebrates has not been reported. While we did not find an important role for MCMDC2 in mitotically dividing cells, our work revealed that MCMDC2 is essential for fertility in both sexes due to a crucial function in meiotic recombination. Meiotic recombination begins with the introduction of DNA double-strand breaks into the genome. DNA ends at break sites are resected. The resultant 3-prime single-stranded DNA overhangs recruit RAD51 and DMC1 recombinases that promote the invasion of homologous duplex DNAs by the resected DNA ends. Multiple strand invasions on each chromosome promote the alignment of homologous chromosomes, which is a prerequisite for inter-homologue crossover formation during meiosis. We found that although DNA ends at break sites were evidently resected, and they recruited RAD51 and DMC1 recombinases, these recombinases were ineffective in promoting alignment of homologous chromosomes in the absence of MCMDC2. Consequently, RAD51 and DMC1 foci, which are thought to mark early recombination intermediates, were abnormally persistent in Mcmdc2-/- meiocytes. Importantly, the strand invasion stabilizing MSH4 protein, which marks more advanced recombination intermediates, did not efficiently form foci in Mcmdc2-/- meiocytes. Thus, our work suggests that MCMDC2 plays an important role in either the formation, or the stabilization, of DNA strand invasion events that promote homologue alignment and provide the basis for inter-homologue crossover formation during meiotic recombination.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Repair of Meiotic DNA Breaks and Homolog Pairing in Mouse Meiosis Requires a Minichromosome Maintenance (MCM) Paralog.Genetics. 2017 Feb;205(2):529-537. doi: 10.1534/genetics.116.196808. Epub 2016 Dec 16. Genetics. 2017. PMID: 27986806 Free PMC article.
-
Meiotic crossover control by concerted action of Rad51-Dmc1 in homolog template bias and robust homeostatic regulation.PLoS Genet. 2013;9(12):e1003978. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003978. Epub 2013 Dec 19. PLoS Genet. 2013. PMID: 24367271 Free PMC article.
-
Down-regulation of Rad51 activity during meiosis in yeast prevents competition with Dmc1 for repair of double-strand breaks.PLoS Genet. 2014 Jan;10(1):e1004005. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004005. Epub 2014 Jan 23. PLoS Genet. 2014. PMID: 24465215 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of RecA homologues Rad51 and Dmc1 during meiotic recombination.Cytogenet Genome Res. 2004;107(3-4):201-7. doi: 10.1159/000080598. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2004. PMID: 15467365 Review.
-
Repair of DNA double-strand breaks in plant meiosis: role of eukaryotic RecA recombinases and their modulators.Plant Reprod. 2023 Mar;36(1):17-41. doi: 10.1007/s00497-022-00443-6. Epub 2022 Jun 1. Plant Reprod. 2023. PMID: 35641832 Review.
Cited by
-
Repair of Meiotic DNA Breaks and Homolog Pairing in Mouse Meiosis Requires a Minichromosome Maintenance (MCM) Paralog.Genetics. 2017 Feb;205(2):529-537. doi: 10.1534/genetics.116.196808. Epub 2016 Dec 16. Genetics. 2017. PMID: 27986806 Free PMC article.
-
Chicory: Understanding the Effects and Effectors of This Functional Food.Nutrients. 2022 Feb 23;14(5):957. doi: 10.3390/nu14050957. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 35267932 Free PMC article.
-
SPO16 binds SHOC1 to promote homologous recombination and crossing-over in meiotic prophase I.Sci Adv. 2019 Jan 23;5(1):eaau9780. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aau9780. eCollection 2019 Jan. Sci Adv. 2019. PMID: 30746471 Free PMC article.
-
UBE2J2 is essential for the progression of meiosis prophase I during spermatogenesis in mice.iScience. 2025 Jun 11;28(8):112878. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2025.112878. eCollection 2025 Aug 15. iScience. 2025. PMID: 40686610 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatics analysis of the transcriptional expression of minichromosome maintenance proteins as potential indicators of survival in patients with cervical cancer.BMC Cancer. 2021 Aug 18;21(1):928. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-08674-y. BMC Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34404366 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

