The Transcriptome of Rhabdomyosarcoma Cells Infected with Cytolytic and Non-Cytolytic Variants of Coxsackievirus B2 Ohio-1
- PMID: 27760161
- PMCID: PMC5070843
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0164548
The Transcriptome of Rhabdomyosarcoma Cells Infected with Cytolytic and Non-Cytolytic Variants of Coxsackievirus B2 Ohio-1
Abstract
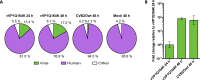
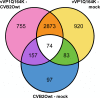
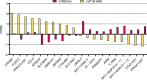
The transcriptomes of cells infected with lytic and non-lytic variants of coxsackievirus B2 Ohio-1 (CVB2O) were analyzed using next generation sequencing. This approach was selected with the purpose of elucidating the effects of lytic and non-lytic viruses on host cell transcription. Total RNA was extracted from infected cells and sequenced. The resulting reads were subsequently mapped against the human and CVB2O genomes. The amount of intracellular RNA was measured, indicating lower proportions of human RNA in the cells infected with the lytic virus compared to the non-lytic virus after 48 hours. This may be explained by reduced activity of the cellular transcription/translation machinery in lytic enteroviral replication due to activities of the enteroviral proteases 2A and/or 3C. Furthermore, differential expression in the cells infected with the two virus variants was identified and a number of transcripts were singled out as possible answers to the question of how the viruses interact with the host cells, resulting in lytic or non-lytic infections.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Cytolytic replication of coxsackievirus B2 in CAR-deficient rhabdomyosarcoma cells.Virus Res. 2005 Nov;113(2):107-15. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2005.04.021. Virus Res. 2005. PMID: 15964091
-
A single coxsackievirus B2 capsid residue controls cytolysis and apoptosis in rhabdomyosarcoma cells.J Virol. 2010 Jun;84(12):5868-79. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02383-09. Epub 2010 Apr 7. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20375176 Free PMC article.
-
Differential display RT-PCR analysis of enterovirus-71-infected rhabdomyosarcoma cells reveals mRNA expression responses of multiple human genes with known and novel functions.Virology. 2002 Mar 30;295(1):147-59. doi: 10.1006/viro.2002.1353. Virology. 2002. PMID: 12033773
-
Therapeutic Use of Native and Recombinant Enteroviruses.Viruses. 2016 Feb 23;8(3):57. doi: 10.3390/v8030057. Viruses. 2016. PMID: 26907330 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a hypothesis of persistent (non-lytic) enteroviral infection.Amyotroph Lateral Scler Other Motor Neuron Disord. 2005 Jun;6(2):77-87. doi: 10.1080/14660820510027026. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Other Motor Neuron Disord. 2005. PMID: 16036430 Review.
References
-
- Pallansch MA, Roos RP. Enteroviruses: polioviruses, coxsackieviruses, echoviruses and newer enteroviruses Fields virology. 5th ed. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2007. p. 839–93.
-
- Racaniello VR. Picornaviridae: The viruses and their replication In: Knipe DM, Howley PM, editors. Fields Virology. 1 5 ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2007.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

