Inhibition of Snail Family Transcriptional Repressor 2 (SNAI2) Enhances Multidrug Resistance of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells
- PMID: 27760172
- PMCID: PMC5070735
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0164752
Inhibition of Snail Family Transcriptional Repressor 2 (SNAI2) Enhances Multidrug Resistance of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells
Abstract
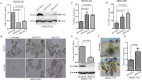
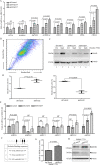
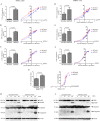
China accounts for almost half of the total number of liver cancer cases and deaths worldwide, and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most primary liver cancer. Snail family transcriptional repressor 2 (SNAI2) is known as an epithelial to mesenchymal transition-inducing transcription factor that drives neoplastic epithelial cells into mesenchymal phenotype. However, the roles of endogenous SNAI2 remain controversial in different types of malignant tumors. Herein, we surprisingly identify that anchorage-independent growth, including the formation of tumor sphere and soft agar colony, is significantly increased when SNAI2 expression is inhibited by shRNAs in HCC cells. Suppression of SNAI2 suffices to up-regulate several cancer stem genes. Although unrelated to the metastatic ability, SNAI2 inhibition does increase the efflux of Hoechst 33342 and enhance multidrug resistance in vitro and in vivo. In agreement with this data, we demonstrate for the first time that decreasing SNAI2 level can transcriptionally upregulate several ATP binding cassette (ABC) transporter genes such as ABCB1. Moreover, ABC transporters' inhibitor verapamil can rescue the multidrug resistance induced by SNAI2 inhibition. Our results implicate that SNAI2 behaves as a tumor suppressor by inhibiting multidrug resistance via suppressing ABC transporter genes in HCC cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Coexpression of gene Oct4 and Nanog initiates stem cell characteristics in hepatocellular carcinoma and promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition through activation of Stat3/Snail signaling.J Hematol Oncol. 2015 Mar 11;8:23. doi: 10.1186/s13045-015-0119-3. J Hematol Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25879771 Free PMC article.
-
SNAI2 upregulation is associated with an aggressive phenotype in fulvestrant-resistant breast cancer cells and is an indicator of poor response to endocrine therapy in estrogen receptor-positive metastatic breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res. 2018 Jun 19;20(1):60. doi: 10.1186/s13058-018-0988-9. Breast Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 29921289 Free PMC article.
-
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase promotes cancer growth and metastasis through upregulation of SNAIL expression.Int J Oncol. 2017 Jan;50(1):252-262. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2016.3774. Epub 2016 Nov 18. Int J Oncol. 2017. PMID: 27878251
-
Overcoming Multidrug Resistance in Cancer Stem Cells.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:635745. doi: 10.1155/2015/635745. Epub 2015 Nov 16. Biomed Res Int. 2015. PMID: 26649310 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SNAI2, a potential crossing point between cancer and cardiovascular disease.FASEB J. 2025 Mar 15;39(5):e70459. doi: 10.1096/fj.202500198R. FASEB J. 2025. PMID: 40059450 Review.
Cited by
-
MYH9 promotes cell metastasis via inducing Angiogenesis and Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Int J Med Sci. 2020 Jul 25;17(13):2013-2023. doi: 10.7150/ijms.46234. eCollection 2020. Int J Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 32788880 Free PMC article.
-
The functions and roles of C2H2 zinc finger proteins in hepatocellular carcinoma.Front Physiol. 2023 Jun 29;14:1129889. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1129889. eCollection 2023. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37457025 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNMT1-maintained hypermethylation of Krüppel-like factor 5 involves in the progression of clear cell renal cell carcinoma.Cell Death Dis. 2017 Jul 27;8(7):e2952. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2017.323. Cell Death Dis. 2017. PMID: 28749461 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of biomarkers associated with partial epithelial to mesenchymal transition in the secretome of slug over-expressing hepatocellular carcinoma cells.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2018 Aug;41(4):439-453. doi: 10.1007/s13402-018-0384-6. Epub 2018 Jun 1. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2018. PMID: 29858962
-
A novel risk model based on anoikis: Predicting prognosis and immune infiltration in cutaneous melanoma.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Jan 16;13:1090857. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1090857. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36726781 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

