Chicken Immune Response after In Ovo Immunization with Chimeric TLR5 Activating Flagellin of Campylobacter jejuni
- PMID: 27760175
- PMCID: PMC5070796
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0164837
Chicken Immune Response after In Ovo Immunization with Chimeric TLR5 Activating Flagellin of Campylobacter jejuni
Abstract
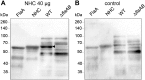
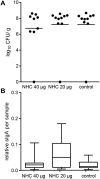
Campylobacter jejuni is the main cause of bacterial food-borne diseases in developed countries. Chickens are the most important source of human infection. Vaccination of poultry is an attractive strategy to reduce the number of C. jejuni in the intestinal tract of chickens. We investigated the immunogenicity and protective efficacy of a recombinant C. jejuni flagellin-based subunit vaccine with intrinsic adjuvant activity. Toll-like receptor activation assays demonstrated the purity and TLR5 stimulating (adjuvant) activity of the vaccine. The antigen (20-40 μg) was administered in ovo to 18 day-old chicken embryos. Serum samples and intestinal content were assessed for antigen-specific systemic and mucosal humoral immune responses. In ovo vaccination resulted in the successful generation of IgY and IgM serum antibodies against the flagellin-based subunit vaccine as determined by ELISA and Western blotting. Vaccination did not induce significant amounts of flagellin-specific secretory IgA in the chicken intestine. Challenge of chickens with C. jejuni yielded similar intestinal colonization levels for vaccinated and control animals. Our results indicate that in ovo delivery of recombinant C. jejuni flagellin subunit vaccine is a feasible approach to yield a systemic humoral immune response in chickens but that a mucosal immune response may be needed to reduce C. jejuni colonization.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chicken immune response following in ovo delivery of bacterial flagellin.Vaccine. 2018 Apr 12;36(16):2139-2146. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2018.02.116. Epub 2018 Mar 9. Vaccine. 2018. PMID: 29530633
-
The specificity of antibody in chickens immunised to reduce intestinal colonisation with Campylobacter jejuni.Vet Microbiol. 1998 Nov;64(1):39-50. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1135(98)00251-x. Vet Microbiol. 1998. PMID: 9874102
-
A DNA prime/protein boost vaccine protocol developed against Campylobacter jejuni for poultry.Vaccine. 2018 Apr 12;36(16):2119-2125. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2018.03.004. Epub 2018 Mar 16. Vaccine. 2018. PMID: 29555216
-
A tolerogenic mucosal immune response leads to persistent Campylobacter jejuni colonization in the chicken gut.Crit Rev Microbiol. 2012 Feb;38(1):17-29. doi: 10.3109/1040841X.2011.615298. Epub 2011 Oct 13. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 21995731 Review.
-
New approaches to development of mucosal vaccine against enteric bacterial pathogens; preventing campylobacteriosis.Pol J Microbiol. 2004;53 Suppl:7-15. Pol J Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15787191 Review.
Cited by
-
Plasmid DNA Prime/Protein Boost Vaccination against Campylobacter jejuni in Broilers: Impact of Vaccine Candidates on Immune Responses and Gut Microbiota.Pharmaceutics. 2023 May 3;15(5):1397. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15051397. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37242639 Free PMC article.
-
Intervention Strategies to Control Campylobacter at Different Stages of the Food Chain.Microorganisms. 2023 Jan 1;11(1):113. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11010113. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 36677405 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vaccinating Meat Chickens against Campylobacter and Salmonella: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Vaccines (Basel). 2022 Nov 15;10(11):1936. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10111936. Vaccines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36423031 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative Transcriptome Analysis Reveals the Innate Immune Response to Mycoplasma gallisepticum Infection in Chicken Embryos and Newly Hatched Chicks.Animals (Basel). 2023 May 17;13(10):1667. doi: 10.3390/ani13101667. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37238096 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of DNA Prime/Protein Boost Vaccination against Campylobacter jejuni on Immune Responses and Gut Microbiota in Chickens.Vaccines (Basel). 2022 Jun 20;10(6):981. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10060981. Vaccines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35746589 Free PMC article.
References
-
- European Food Safety Authority. Scientific opinion on Campylobacter in broiler meat production: control options and performance objectives and/or targets at different stages of the food chain. EFSA Journal. 2011;9: 2105 10.2903/j.efsa.2011.2105 - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

