Genetically Engineered Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 Synbiotics Reduce Metabolic Effects Induced by Chronic Consumption of Dietary Fructose
- PMID: 27760187
- PMCID: PMC5070853
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0164860
Genetically Engineered Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 Synbiotics Reduce Metabolic Effects Induced by Chronic Consumption of Dietary Fructose
Abstract
Aims: To assess protective efficacy of genetically modified Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 (EcN) on metabolic effects induced by chronic consumption of dietary fructose.
Materials and methods: EcN was genetically modified with fructose dehydrogenase (fdh) gene for conversion of fructose to 5-keto-D-fructose and mannitol-2-dehydrogenase (mtlK) gene for conversion to mannitol, a prebiotic. Charles foster rats weighing 150-200 g were fed with 20% fructose in drinking water for two months. Probiotic treatment of EcN (pqq), EcN (pqq-glf-mtlK), EcN (pqq-fdh) was given once per week 109 cells for two months. Furthermore, blood and liver parameters for oxidative stress, dyslipidemia and hyperglycemia were estimated. Fecal samples were collected to determine the production of short chain fatty acids and pyrroloquinoline quinone (PQQ) production.
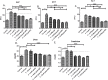
Results: EcN (pqq-glf-mtlK), EcN (pqq-fdh) transformants were confirmed by restriction digestion and functionality was checked by PQQ estimation and HPLC analysis. There was significant increase in body weight, serum glucose, liver injury markers, lipid profile in serum and liver, and decrease in antioxidant enzyme activity in high-fructose-fed rats. However the rats treated with EcN (pqq-glf-mtlK) and EcN (pqq-fdh) showed significant reduction in lipid peroxidation along with increase in serum and hepatic antioxidant enzyme activities. Restoration of liver injury marker enzymes was also seen. Increase in short chain fatty acids (SCFA) demonstrated the prebiotic effects of mannitol and gluconic acid.
Conclusions: Our study demonstrated the effectiveness of probiotic EcN producing PQQ and fructose metabolizing enzymes against the fructose induced hepatic steatosis suggesting that its potential for use in treating fructose induced metabolic syndrome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Genetically engineered Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 synbiotic counters fructose-induced metabolic syndrome and iron deficiency.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2017 Jun;101(11):4713-4723. doi: 10.1007/s00253-017-8207-7. Epub 2017 Mar 10. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2017. PMID: 28283693
-
Pyrroloquinoline quinone-secreting probiotic Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 ameliorates ethanol-induced oxidative damage and hyperlipidemia in rats.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2014 Jul;38(7):2127-37. doi: 10.1111/acer.12456. Epub 2014 Jun 13. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2014. PMID: 24930470
-
Pyrroloquinoline quinone (PQQ) producing Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 (EcN) alleviates age associated oxidative stress and hyperlipidemia, and improves mitochondrial function in ageing rats.Exp Gerontol. 2015 Jun;66:1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2015.04.001. Epub 2015 Apr 2. Exp Gerontol. 2015. PMID: 25843018
-
Genetic engineering of probiotic Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 for clinical application.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2016 Oct;100(20):8693-9. doi: 10.1007/s00253-016-7829-5. Epub 2016 Sep 17. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 27640192 Review.
-
Prospective and challenges of live bacterial therapeutics from a superhero Escherichia coli Nissle 1917.Crit Rev Microbiol. 2023 Sep;49(5):611-627. doi: 10.1080/1040841X.2022.2109405. Epub 2022 Aug 10. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 35947523 Review.
Cited by
-
High-quality genome-scale metabolic network reconstruction of probiotic bacterium Escherichia coli Nissle 1917.BMC Bioinformatics. 2022 Dec 30;23(1):566. doi: 10.1186/s12859-022-05108-9. BMC Bioinformatics. 2022. PMID: 36585633 Free PMC article.
-
Next-Generation Probiotics as Novel Therapeutics for Improving Human Health: Current Trends and Future Perspectives.Microorganisms. 2024 Feb 20;12(3):430. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12030430. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 38543481 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Meta-analysis of the effects of probiotics on hyperlipidemia.Curr Res Food Sci. 2024 Oct 15;9:100885. doi: 10.1016/j.crfs.2024.100885. eCollection 2024. Curr Res Food Sci. 2024. PMID: 39469722 Free PMC article.
-
A molecular toolkit for heterologous protein secretion across Bacteroides species.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Dec 15:2023.12.14.571725. doi: 10.1101/2023.12.14.571725. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Nat Commun. 2024 Nov 11;15(1):9741. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-53845-7. PMID: 38168418 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Synthetic Biology Approaches in The Development of Engineered Therapeutic Microbes.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 19;21(22):8744. doi: 10.3390/ijms21228744. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33228099 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Busserolles J, Gueux E, Rock E, Mazur A, Rayssiguier Y . High fructose feeding of magnesium deficient rats is associated with increased plasma triglyceride concentration and increased oxidative stress. Magnesium Research. 2003. March 1; 16(1):7–12. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

