Genotyping and Descriptive Proteomics of a Potential Zoonotic Canine Strain of Giardia duodenalis, Infective to Mice
- PMID: 27760188
- PMCID: PMC5070761
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0164946
Genotyping and Descriptive Proteomics of a Potential Zoonotic Canine Strain of Giardia duodenalis, Infective to Mice
Abstract
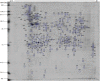
The zoonotic potential of giardiasis, as proposed by WHO since the late 70's, has been largely confirmed in this century. The genetic assemblages A and B of Giardia duodenalis are frequently isolated from human and canine hosts. Most of the assemblage A strains are not infective to adult mice, which can limit the range of studies regarding to biology of G. duodenalis, including virulence factors and the interaction with host immune system. This study aimed to determine the infectivity in mice of an assemblage A Giardia duodenalis strain (BHFC1) isolated from a dog and to classify the strain in sub-assemblages (AI, AII, AIII) through the phylogenetic analysis of beta-giardin (bg), triose phosphate isomerase (tpi) and glutamate dehydrogenase (gdh) genes. In addition, the proteomic profile of soluble and insoluble protein fractions of trophozoites was analyzed by 2D-electrophoresis. Accordingly, trophozoites of BHFC1 were highly infective to Swiss mice. The phylogenetic analysis of tpi and gdh revealed that BHFC1 clustered to sub-assemblage AI. The proteomic map of soluble and insoluble protein fractions led to the identification of 187 proteins of G. duodenalis, 27 of them corresponding to hypothetical proteins. Considering both soluble and soluble fractions, the vast majority of the identified proteins (n = 82) were classified as metabolic proteins, mainly associated with carbon and lipid metabolism, including 53 proteins with catalytic activity. Some of the identified proteins correspond to antigens while others can be correlated with virulence. Besides a significant complementation to the proteomic data of G. duodenalis, these data provide an important source of information for future studies on various aspects of the biology of this parasite, such as virulence factors and host and pathogen interactions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Infection rate and genetic diversity of Giardia duodenalis in pet and stray dogs in Henan Province, China.Parasitol Int. 2016 Apr;65(2):159-62. doi: 10.1016/j.parint.2015.11.008. Epub 2015 Nov 26. Parasitol Int. 2016. PMID: 26631754
-
Multilocus genotyping of Giardia duodenalis isolates from calves in Oromia Special Zone, Central Ethiopia.Infect Genet Evol. 2016 Sep;43:281-8. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2016.06.005. Epub 2016 Jun 4. Infect Genet Evol. 2016. PMID: 27268147
-
Detection and multilocus genotyping of Giardia duodenalis in dogs in Sichuan province, China.Parasite. 2017;24:31. doi: 10.1051/parasite/2017032. Epub 2017 Aug 3. Parasite. 2017. PMID: 28770713 Free PMC article.
-
Giardia duodenalis genetic assemblages and hosts.Parasite. 2016;23:13. doi: 10.1051/parasite/2016013. Epub 2016 Mar 16. Parasite. 2016. PMID: 26984116 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Host specificity in the Giardia duodenalis species complex.Infect Genet Evol. 2018 Dec;66:335-345. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2017.12.001. Epub 2017 Dec 7. Infect Genet Evol. 2018. PMID: 29225147 Review.
Cited by
-
Membrane-Associated Proteins in Giardia lamblia.Genes (Basel). 2018 Aug 10;9(8):404. doi: 10.3390/genes9080404. Genes (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30103435 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Novel Nano Magnetic Beads Dot ELISA Immunoassay and Its Application on the Detection of Giardia lamblia Coproantigen.Iran J Parasitol. 2018 Oct-Dec;13(4):532-540. Iran J Parasitol. 2018. PMID: 30697306 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in the Giardia-host relationship reveal danger lurking behind the smile.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2018 Sep 6;12(9):e0006625. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0006625. eCollection 2018 Sep. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2018. PMID: 30188894 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Applied Proteomics in 'One Health'.Proteomes. 2021 Jun 30;9(3):31. doi: 10.3390/proteomes9030031. Proteomes. 2021. PMID: 34208880 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Giardiasis as a neglected disease in Brazil: Systematic review of 20 years of publications.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2017 Oct 24;11(10):e0006005. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0006005. eCollection 2017 Oct. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2017. PMID: 29065126 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Farthing MJ. Host-parasite interactions in human giardiasis. The Quarterly journal of medicine. 1989;70(263):191–204. . - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

