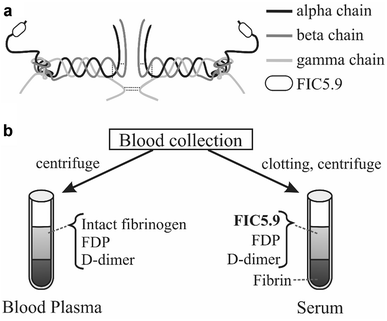
Fibrinogen alpha C chain 5.9 kDa fragment (FIC5.9), a biomarker for various pathological conditions, is produced in post-blood collection by fibrinolysis and coagulation factors
- PMID: 27761105
- PMCID: PMC5055723
- DOI: 10.1186/s12014-016-9129-6
Fibrinogen alpha C chain 5.9 kDa fragment (FIC5.9), a biomarker for various pathological conditions, is produced in post-blood collection by fibrinolysis and coagulation factors
Abstract
Background: Fibrinogen alpha C chain 5.9 kDa fragment (FIC5.9) is a new serum biomarker for chronic hepatitis that was discovered by proteomics analysis. Previous studies have shown that FIC5.9 is derived from the C-terminal region of fibrinogen alpha chain and the serum levels of FIC5.9 decrease in chronic hepatitis. It also have been reported that FIC5.9 cannot be detected in the blood stream of the systemic circulation and it is released from fibrinogen during blood clotting in collecting tube. However, the mechanism of FIC5.9 releasing from fibrinogen is unclear.
Methods: We formulated a hypothesis that FIC5.9 is released by enzymes that are activated by post-blood collection and may be coagulation and fibrinolysis factors. In this study, we analyzed the mechanisms of FIC5.9 releasing from fibrinogen in healthy blood.
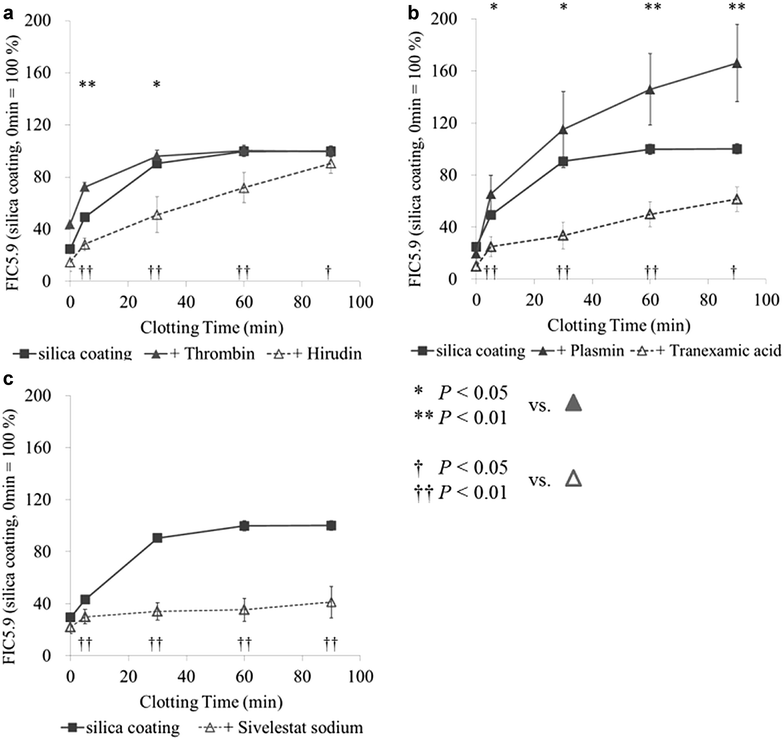
Results: Our analysis showed that thrombin acts as an initiator for FIC5.9 releasing, and that mainly plasmin cleaves N-terminal end of FIC5.9 and neutrophil elastase cleave C-terminal end of FIC5.9.
Conclusion: FIC5.9 reflects minute changes in coagulation and fibrinolysis factors and may be associated with pathological conditions.
Keywords: Fibrinogen alpha C chain 5.9 kDa fragment (FIC5.9); Biomarker; Coagulation; Fibrinogen; Hepatitis; Plasmin; Thrombin.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Development of a sandwich ELISA for the 5.9-kDa fibrinogen alpha C chain fragment detected by serum proteome analysis.Proteomics Clin Appl. 2011 Apr;5(3-4):141-6. doi: 10.1002/prca.201000127. Epub 2011 Mar 1. Proteomics Clin Appl. 2011. PMID: 21360827
-
Disseminated intravascular coagulation at an early phase of trauma is associated with consumption coagulopathy and excessive fibrinolysis both by plasmin and neutrophil elastase.Surgery. 2011 Feb;149(2):221-30. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2010.06.010. Epub 2010 Jul 23. Surgery. 2011. PMID: 20655560
-
Impaired coagulation of fibrinogen due to digestion of the C-terminal end of the A alpha-chain by human neutrophil elastase.Thromb Res. 1994 Jan 1;73(1):61-8. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(94)90054-x. Thromb Res. 1994. PMID: 8178314
-
Thrombin-activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor.Curr Med Chem. 2004 Sep;11(17):2335-48. doi: 10.2174/0929867043364586. Curr Med Chem. 2004. PMID: 15379716 Review.
-
[Regulatory mechanism of fibrinolysis system by thrombin activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor (TAFI)].Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2000 Nov;116(5):298-303. doi: 10.1254/fpj.116.298. Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2000. PMID: 11215380 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Serum peptides as candidate biomarkers for relapsing polychondritis.J Mass Spectrom Adv Clin Lab. 2025 Apr 30;37:28-38. doi: 10.1016/j.jmsacl.2025.04.001. eCollection 2025 Aug. J Mass Spectrom Adv Clin Lab. 2025. PMID: 40486527 Free PMC article.
-
FGA influences invasion and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma through the PI3K/AKT pathway.Aging (Albany NY). 2024 Jul 9;16(19):12806-12819. doi: 10.18632/aging.206011. Epub 2024 Jul 9. Aging (Albany NY). 2024. PMID: 39227068 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Umemura H, Nezu M, Satoh M, Kimura A, et al. Effects of the time intervals between venipuncture and serum preparation for serum peptidome analysis by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Clin Chim Acta. 2009;406:179–180. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2009.06.007. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
