Carotid Stent Fracture from Stylocarotid Syndrome
- PMID: 27761179
- PMCID: PMC5065264
- DOI: 10.3941/jrcr.v10i6.1618
Carotid Stent Fracture from Stylocarotid Syndrome
Abstract
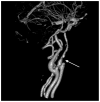
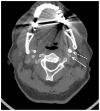
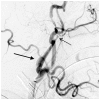
Eagle syndrome is a rare condition resulting from elongation of the temporal styloid process or calcification of its associated stylohyoid ligaments. Although usually presenting with pain or odynophagia, Eagle syndrome has been reported to cause a multitude of neurologic symptoms or vascular complications, some of which can be life-threatening. We present a case in which an endovascularly placed internal carotid artery stent in close proximity to a calcified stylohyoid ligament resulted in stent fracture with subsequent stent and vessel occlusion. We review and discuss the presentation, diagnosis, etiology, complications and treatment options of the syndrome.
Keywords: CT; Eagle syndrome; carotid stent; stent fracture; stylocarotid syndrome.
Figures

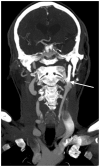
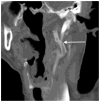


References
-
- Mupparapu M, Robinson MD. The mineralized and elongated styloid process: a review of current diagnostic criteria and evaluation strategies. Gen Dent. 2005;53(1):54–59. - PubMed
-
- Eagle WW. Elongated styloid process: Report of two cases. Arch Otolaryngol. 1937;25:584–587. - PubMed
-
- Martin TJ, Friedland DR, Merati AL. Transcervical resection of the styloid process in Eagle syndrome. Ear Nose Throat J. 2008;87(7):399–401. - PubMed
-
- Beder E, Ozgursoy OB, Ozgursoy SK, Anadolu Y. Three-dimensional computed tomography and surgical treatment for Eagle’s syndrome. Ear Nose Throat J. 2006;85(7):443–445. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources