Infliximab Modulates Cisplatin-Induced Hepatotoxicity in Rats
- PMID: 27761277
- PMCID: PMC5056652
- DOI: 10.5152/balkanmedj.2016.150576
Infliximab Modulates Cisplatin-Induced Hepatotoxicity in Rats
Abstract
Background: Cisplatin (Cis) is one of the most commonly used antineoplastic drugs. It is used as chemotherapy for many solid organ malignancies such as brain, neck, male and female urogenital, vesical and pulmonary cancers. Infliximab blocks tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α). Several studies have reported that infliximab ameliorates cell damage by reducing cytokine levels.
Aims: We aimed to investigate whether infliximab has a preventive effect against cisplatin-induced hepatotoxicity and whether it has a synergistic effect when combined with Cis.
Study design: Animal experimentation.
Methods: Male Wistar albino rats were divided in three groups as follows: Cis group, infliximab + Cis (CIN) group and the control group. Each group comprised 10 animals. Animals in the Cis group received an intraperitoneal single-dose injection of Cis (7 mg/kg). In the CIN group, a single dose of infliximab (7 mg/kg) was administered 72 h prior to the Cis injection. After 72 h, a single dose of Cis (7 mg/kg) was administered. All rats were sacrificed five days after Cis injection.
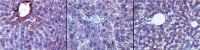
Results: TNF-α levels in the Cis group were significantly higher (345.5±40.0 pg/mg protein) than those of the control (278.7±62.1 pg/mg protein, p=0.003) and CIN groups (239.0±64.2 pg/mg protein, p=0.013). The Cis group was found to have high carbonic anhydrase (CA)-II and low carbamoyl phosphate synthetase-1 (CPS-1) levels. Aspartate transaminase (AST) and alanine transaminase (ALT) levels were lower in the CIN group as compared to the Cis group. Total histological damage was greater in the Cis group as compared to the control and CIN groups.
Conclusion: Cis may lead to liver damage by increasing cytokine levels. It may increase oxidative stress-induced tissue damage by increasing carbonic anhydrase II (CA-II) enzyme levels and decreasing CPS-1 enzyme levels. Infliximab decreases Cis-induced hepatic damage by blocking TNF-α and it may also protect against liver damage by regulating CPS-1 and CA-II enzyme levels.
Keywords: Carbamoyl-phosphate synthetase 1; carbonic anhydrase; cisplatin; hepatotoxicity; infliximab; tumor necrosis factor alpha.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflict of interest was declared by the authors.
Figures


References
-
- Bentli R, Parlakpinar H, Polat A, Samdanci E, Sarihan ME, Sagir M. Molsidomine prevents cisplatin-induced hepatotoxicity. Arch Med Res. 2013;44:521–28. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.arcmed.2013.09.013. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Waseem M, Parvez S. Mitochondrial dysfunction mediated cisplatin induced toxicity: modulatory role of curcumin. Food Chem Toxicol. 2013;53:334–42. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2012.11.055. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Karadeniz A, Simsek N, Karakus E, Yildirim S, Kara A, Can I, et al. Royal jelly modulates oxidative stress and apoptosis in liver and kidneys of rats treated with cisplatin. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2011 981793. http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2011/981793. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ferah I, Halici Z, Bayir Y, Demirci E, Unal B, Cadirci E. The role of infliximab on paracetamol-induced hepatotoxicity in rats. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2013;35:373–81. http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/08923973.2013.775589. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mahmoud MF, El Shazly SM, Barakat W. Inhibition of TNF-α protects against hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats via NF-κB dependent pathway. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2012;385:465–71. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00210-012-0729-z. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
