Evaluating pH in the Extracellular Tumor Microenvironment Using CEST MRI and Other Imaging Methods
- PMID: 27761517
- PMCID: PMC5066878
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/206405
Evaluating pH in the Extracellular Tumor Microenvironment Using CEST MRI and Other Imaging Methods
Abstract
Tumor acidosis is a consequence of altered metabolism, which can lead to chemoresistance and can be a target of alkalinizing therapies. Noninvasive measurements of the extracellular pH (pHe) of the tumor microenvironment can improve diagnoses and treatment decisions. A variety of noninvasive imaging methods have been developed for measuring tumor pHe. This review provides a detailed description of the advantages and limitations of each method, providing many examples from previous research reports. A substantial emphasis is placed on methods that use MR spectroscopy and MR imaging, including recently developed methods that use chemical exchange saturation transfer MRI that combines some advantages of MR spectroscopy and imaging. Together, this review provides a comprehensive overview of methods for measuring tumor pHe, which may facilitate additional creative approaches in this research field.
Figures








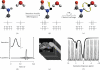
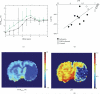
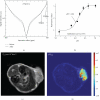




References
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011;144(5):646–674. - PubMed
-
- Beddek AJ, Rawson P, Peng L, et al. Profiling the metabolic proteome of bovine mammary tissue. Proteomics. 2008;8(7):1502–1515. - PubMed
-
- Warburg O. On the origin of cancer cells. Science. 1956;123(3191):309–314. - PubMed
-
- Gillies RJ, Raghunand N, Garcia-Martin ML, Gatenby RA. pH imaging. IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Magazine. 2004;23(5):57–64. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
