A case of pembrolizumab-induced type-1 diabetes mellitus and discussion of immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced type 1 diabetes
- PMID: 27761609
- PMCID: PMC11028603
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-016-1913-7
A case of pembrolizumab-induced type-1 diabetes mellitus and discussion of immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced type 1 diabetes
Abstract
Immune checkpoint inhibitors such as pembrolizumab, ipilimumab, and nivolumab, now FDA-approved for use in treating several types of cancer, have been associated with immune-related adverse effects. Specifically, the antibodies targeting the programmed-cell death-1 immune checkpoint, pembrolizumab and nivolumab, have been rarely reported to induce the development of type 1 diabetes mellitus. Here we describe a case of a patient who developed antibody-positive type 1 diabetes mellitus following treatment with pembrolizumab in combination with systemic chemotherapy for metastatic adenocarcinoma of the lung. We will also provide a brief literature review of other rarely reported cases of type 1 diabetes presenting after treatment with pembrolizumab and nivolumab, as well as discussion regarding potential mechanisms of this adverse effect and its importance as these drugs continue to become even more widespread.
Keywords: Diabetes mellitus; Immune-related adverse effect; Immunomodulatory; Ipilimumab; Nivolumab; Pembrolizumab.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
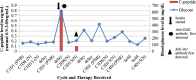
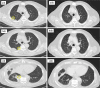
Similar articles
-
Diabetic ketoacidosis induced by a single dose of pembrolizumab.Am J Emerg Med. 2019 Feb;37(2):376.e1-376.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2018.10.040. Epub 2018 Oct 21. Am J Emerg Med. 2019. PMID: 30361152
-
Nivolumab-induced autoimmune diabetes mellitus presenting as diabetic ketoacidosis in a patient with metastatic lung cancer.J Immunother Cancer. 2017 May 16;5:40. doi: 10.1186/s40425-017-0245-2. eCollection 2017. J Immunother Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28515940 Free PMC article.
-
Programmed Cell Death-1 Inhibitor-Induced Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2018 Sep 1;103(9):3144-3154. doi: 10.1210/jc.2018-00728. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2018. PMID: 29955867 Review.
-
Combined immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy with nivolumab and ipilimumab causing acute-onset type 1 diabetes mellitus following a single administration: two case reports.BMC Endocr Disord. 2019 Dec 23;19(1):144. doi: 10.1186/s12902-019-0467-z. BMC Endocr Disord. 2019. PMID: 31870373 Free PMC article.
-
Current status and future directions of the immune checkpoint inhibitors ipilimumab, pembrolizumab, and nivolumab in oncology.Ann Pharmacother. 2015 Aug;49(8):907-37. doi: 10.1177/1060028015586218. Epub 2015 May 19. Ann Pharmacother. 2015. PMID: 25991832 Review.
Cited by
-
Immune checkpoint inhibitors associated cardiovascular immune-related adverse events.Front Immunol. 2024 Feb 5;15:1340373. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1340373. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38375475 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunotherapy-Associated Pancreatic Adverse Events: Current Understanding of Their Mechanism, Diagnosis, and Management.Front Oncol. 2021 Feb 25;11:627612. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.627612. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33732647 Free PMC article.
-
Cases from the Immune-Related Adverse Event Tumor Board: Diagnosis and Management of Immune Checkpoint Blockade-Induced Diabetes.Oncologist. 2020 Nov;25(11):921-924. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2019-0806. Epub 2020 Jul 7. Oncologist. 2020. PMID: 32564463 Free PMC article.
-
Occurrence of Type 1 Diabetes in A Patient Enrolled in An Immunotherapy Combination Phase 1 Clinical Trial: A Case Study.Asia Pac J Oncol Nurs. 2021 Apr 24;8(6):737-739. doi: 10.4103/apjon.apjon-2122. eCollection 2021 Nov-Dec. Asia Pac J Oncol Nurs. 2021. PMID: 34790859 Free PMC article.
-
Unravelling Checkpoint Inhibitor Associated Autoimmune Diabetes: From Bench to Bedside.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Nov 5;12:764138. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.764138. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34803927 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Yamazaki N, Kiyohara Y, Uhara H, Fukushima S, Uchi H, Shibagaki N, Tsutsumida A, Yoshikawa S, Okuyama R, Ito Y, Tokudome T. Phase II study of ipilimumab monotherapy in Japanese patients with advanced melanoma. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2015;76(5):997–1004. doi: 10.1007/s00280-015-2873-x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Keytruda (pembrolizumab) (2014) [package insert] Merck & Co., Inc., Whitehouse Station, NJ
-
- Opdivo (nivolumab) (2014) [package insert] Bristol-Myers Squibb Company, Princeton, NJ
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

