Quantitative interaction mapping reveals an extended UBX domain in ASPL that disrupts functional p97 hexamers
- PMID: 27762274
- PMCID: PMC5080433
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms13047
Quantitative interaction mapping reveals an extended UBX domain in ASPL that disrupts functional p97 hexamers
Abstract
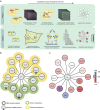
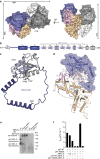
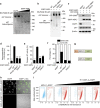
Interaction mapping is a powerful strategy to elucidate the biological function of protein assemblies and their regulators. Here, we report the generation of a quantitative interaction network, directly linking 14 human proteins to the AAA+ ATPase p97, an essential hexameric protein with multiple cellular functions. We show that the high-affinity interacting protein ASPL efficiently promotes p97 hexamer disassembly, resulting in the formation of stable p97:ASPL heterotetramers. High-resolution structural and biochemical studies indicate that an extended UBX domain (eUBX) in ASPL is critical for p97 hexamer disassembly and facilitates the assembly of p97:ASPL heterotetramers. This spontaneous process is accompanied by a reorientation of the D2 ATPase domain in p97 and a loss of its activity. Finally, we demonstrate that overproduction of ASPL disrupts p97 hexamer function in ERAD and that engineered eUBX polypeptides can induce cell death, providing a rationale for developing anti-cancer polypeptide inhibitors that may target p97 activity.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

