Universal stress protein Rv2624c alters abundance of arginine and enhances intracellular survival by ATP binding in mycobacteria
- PMID: 27762279
- PMCID: PMC5071874
- DOI: 10.1038/srep35462
Universal stress protein Rv2624c alters abundance of arginine and enhances intracellular survival by ATP binding in mycobacteria
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Universal stress protein Rv2624c alters abundance of arginine and enhances intracellular survival by ATP binding in mycobacteria.Sci Rep. 2017 Mar 22;7:44966. doi: 10.1038/srep44966. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28327673 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
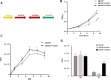
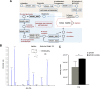
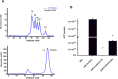
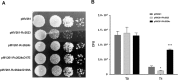
The universal stress protein family is a family of stress-induced proteins. Universal stress proteins affect latency and antibiotic resistance in mycobacteria. Here, we showed that Mycobacterium smegmatis overexpressing M. tuberculosis universal stress protein Rv2624c exhibits increased survival in human monocyte THP-1 cells. Transcriptome analysis suggested that Rv2624c affects histidine metabolism, and arginine and proline metabolism. LC-MS/MS analysis showed that Rv2624c affects the abundance of arginine, a modulator of both mycobacteria and infected THP-1 cells. Biochemical analysis showed that Rv2624c is a nucleotide-binding universal stress protein, and an Rv2624c mutant incapable of binding ATP abrogated the growth advantage in THP-1 cells. Rv2624c may therefore modulate metabolic pathways in an ATP-dependent manner, changing the abundance of arginine and thus increasing survival in THP-1 cells.
Figures

References
-
- Eurosurveillance editorial, t. WHO publishes Global tuberculosis report 2013. Euro Surveill 18 ( 2013). - PubMed
-
- Flynn J. L. & Chan J. Immunology of tuberculosis. Annu Rev Immunol 19, 93–129 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Nystrom T. & Neidhardt F. C. Cloning, mapping and nucleotide sequencing of a gene encoding a universal stress protein in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol 6, 3187–3198 (1992). - PubMed
-
- Diez A., Gustavsson N. & Nystrom T. The universal stress protein A of Escherichia coli is required for resistance to DNA damaging agents and is regulated by a RecA/FtsK-dependent regulatory pathway. Mol Microbiol 36, 1494–1503 (2000). - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

