Inducing G2/M Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis through Generation Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)-Mediated Mitochondria Pathway in HT-29 Cells by Dentatin (DEN) and Dentatin Incorporated in Hydroxypropyl-β-Cyclodextrin (DEN-HPβCD)
- PMID: 27763535
- PMCID: PMC5085686
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms17101653
Inducing G2/M Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis through Generation Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)-Mediated Mitochondria Pathway in HT-29 Cells by Dentatin (DEN) and Dentatin Incorporated in Hydroxypropyl-β-Cyclodextrin (DEN-HPβCD)
Abstract
Dentatin (DEN), purified from the roots of Clausena excavata Burm f., has poor aqueous solubility that reduces its therapeutic application. The aim of this study was to assess the effects of DEN-HPβCD (hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin) complex as an anticancer agent in HT29 cancer cell line and compare with a crystal DEN in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO). The exposure of the cancer cells to DEN or DEN-HPβCD complex leads to cell growth inhibition as determined by MTT (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide) assay. To analyze the mechanism, in which DEN or DEN-HPβCD complex causes the death in human colon HT29 cancer cells, was evaluated by the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELIZA)-based assays for caspase-3, 8, 9, and reactive oxygen species (ROS). The findings showed that an anti-proliferative effect of DEN or DEN-HPβCD complex were via cell cycle arrest at the G2/M phase and eventually induced apoptosis through both mitochondrial and extrinsic pathways. The down-regulation of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) which leaded to apoptosis upon treatment, was investigated by Western-blotting. Hence, complexation between DEN and HPβCD did not diminish or eliminate the effective properties of DEN as anticancer agent. Therefore, it would be possible to resolve the conventional and current issues associated with the development and commercialization of antineoplastic agents in the future.
Keywords: Dentatin; apoptosis; cytostatic; cytotoxicity; reactive oxygen species (ROS).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures









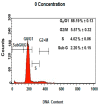


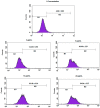

References
-
- Arbab I.A., Looi C.Y., Abdul A.B., Cheah F.K., Wong W.F., Sukari M.A., Abdullah R., Mohan S., Syam S., Arya A. Dentatin induces apoptosis in prostate cancer cells via Bcl-2, Bcl-xL, survivin downregulation, caspase-9,-3/7 activation, and NF-κB inhibition. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2012 doi: 10.1155/2012/856029. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

