Cross-Neutralisation of In Vitro Neurotoxicity of Asian and Australian Snake Neurotoxins and Venoms by Different Antivenoms
- PMID: 27763543
- PMCID: PMC5086662
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins8100302
Cross-Neutralisation of In Vitro Neurotoxicity of Asian and Australian Snake Neurotoxins and Venoms by Different Antivenoms
Abstract
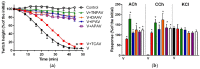
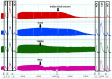
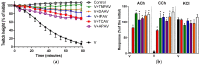
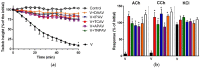
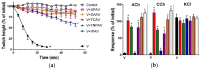
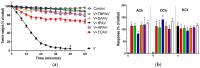
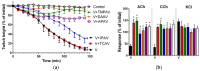
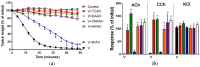
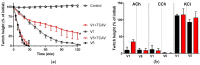
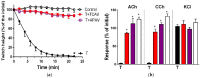
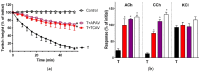
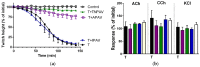
There is limited information on the cross-neutralisation of neurotoxic venoms with antivenoms. Cross-neutralisation of the in vitro neurotoxicity of four Asian and four Australian snake venoms, four post-synaptic neurotoxins (α-bungarotoxin, α-elapitoxin-Nk2a, α-elapitoxin-Ppr1 and α-scutoxin; 100 nM) and one pre-synaptic neurotoxin (taipoxin; 100 nM) was studied with five antivenoms: Thai cobra antivenom (TCAV), death adder antivenom (DAAV), Thai neuro polyvalent antivenom (TNPAV), Indian Polyvalent antivenom (IPAV) and Australian polyvalent antivenom (APAV). The chick biventer cervicis nerve-muscle preparation was used for this study. Antivenom was added to the organ bath 20 min prior to venom. Pre- and post-synaptic neurotoxicity of Bungarus caeruleus and Bungarus fasciatus venoms was neutralised by all antivenoms except TCAV, which did not neutralise pre-synaptic activity. Post-synaptic neurotoxicity of Ophiophagus hannah was neutralised by all antivenoms, and Naja kaouthia by all antivenoms except IPAV. Pre- and post-synaptic neurotoxicity of Notechis scutatus was neutralised by all antivenoms, except TCAV, which only partially neutralised pre-synaptic activity. Pre- and post-synaptic neurotoxicity of Oxyuranus scutellatus was neutralised by TNPAV and APAV, but TCAV and IPAV only neutralised post-synaptic neurotoxicity. Post-synaptic neurotoxicity of Acanthophis antarcticus was neutralised by all antivenoms except IPAV. Pseudonaja textillis post-synaptic neurotoxicity was only neutralised by APAV. The α-neurotoxins were neutralised by TNPAV and APAV, and taipoxin by all antivenoms except IPAV. Antivenoms raised against venoms with post-synaptic neurotoxic activity (TCAV) cross-neutralised the post-synaptic activity of multiple snake venoms. Antivenoms raised against pre- and post-synaptic neurotoxic venoms (TNPAV, IPAV, APAV) cross-neutralised both activities of Asian and Australian venoms. While acknowledging the limitations of adding antivenom prior to venom in an in vitro preparation, cross-neutralization of neurotoxicity means that antivenoms from one region may be effective in other regions which do not have effective antivenoms. TCAV only neutralized post-synaptic neurotoxicity and is potentially useful in distinguishing pre-synaptic and post-synaptic effects in the chick biventer cervicis preparation.
Keywords: antivenom; cross-neutralisation; neurotoxicity; snake; venom.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
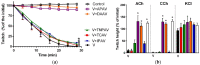


References
-
- Kasturiratne A., Wickremasinghe A.R., De Silva N., Gunawardena N.K., De Silva N., Pathmeswaran A., Premaratna R., Savioli L., Lalloo D.G., De Silva H.J. The global burden of snakebite: A literature analysis and modelling based on regional estimates of envenoming and deaths. PLoS Med. 2008;5:302. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0050218. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

