Role of non-coding RNA transcription around gene regulatory elements in transcription factor recruitment
- PMID: 27763805
- PMCID: PMC5270525
- DOI: 10.1080/15476286.2016.1248020
Role of non-coding RNA transcription around gene regulatory elements in transcription factor recruitment
Abstract
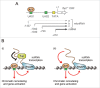
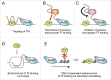
Eukaryotic cells produce a variety of non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs), many of which have been shown to play pivotal roles in biological processes such as differentiation, maintenance of pluripotency of stem cells, and cellular response to various stresses. Genome-wide analyses have revealed that many ncRNAs are transcribed around regulatory DNA elements located proximal or distal to gene promoters, but their biological functions are largely unknown. Recently, it has been demonstrated in yeast and mouse that ncRNA transcription around gene promoters and enhancers facilitates DNA binding of transcription factors to their target sites. These results suggest universal roles of promoter/enhancer-associated ncRNAs in the recruitment of transcription factors to their binding sites.
Keywords: Corepressor; enhancer; gene expression; ncRNA; promoter; transcription factor.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Enhancers as non-coding RNA transcription units: recent insights and future perspectives.Nat Rev Genet. 2016 Apr;17(4):207-23. doi: 10.1038/nrg.2016.4. Epub 2016 Mar 7. Nat Rev Genet. 2016. PMID: 26948815 Review.
-
Transposable Elements and DNA Methylation Create in Embryonic Stem Cells Human-Specific Regulatory Sequences Associated with Distal Enhancers and Noncoding RNAs.Genome Biol Evol. 2015 May 7;7(6):1432-54. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evv081. Genome Biol Evol. 2015. PMID: 25956794 Free PMC article.
-
Non-coding transcription at cis-regulatory elements: computational and experimental approaches.Methods. 2013 Sep 1;63(1):66-75. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2013.03.021. Epub 2013 Mar 29. Methods. 2013. PMID: 23542771
-
Noncoding RNAs: Regulators of the Mammalian Transcription Machinery.J Mol Biol. 2016 Jun 19;428(12):2652-2659. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2016.02.019. Epub 2016 Feb 23. J Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 26920110 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The ribosomal protein rpl26 promoter is required for its 3' sense terminus ncRNA transcription in Schizosaccharomyces pombe, implicating a new transcriptional mechanism for ncRNAs.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014 Jan 31;444(1):86-91. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.01.018. Epub 2014 Jan 14. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014. PMID: 24434141
Cited by
-
Identification and analysis of spinal cord injury subtypes using weighted gene co-expression network analysis.Ann Transl Med. 2021 Mar;9(6):466. doi: 10.21037/atm-21-340. Ann Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 33850863 Free PMC article.
-
The Long Non-coding RNA SNHG12 Functions as a Competing Endogenous RNA to Modulate the Progression of Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury.Mol Neurobiol. 2022 Feb;59(2):1073-1087. doi: 10.1007/s12035-021-02648-8. Epub 2021 Nov 27. Mol Neurobiol. 2022. PMID: 34839459
-
Long Non-coding RNA PVT1 Inhibits miR-30c-5p to Upregulate Rock2 to Modulate Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury Through MAPK Signaling Pathway Activation.Mol Neurobiol. 2021 Nov;58(11):6032-6048. doi: 10.1007/s12035-021-02539-y. Epub 2021 Aug 26. Mol Neurobiol. 2021. PMID: 34436749
-
Functional and transcriptional profiling of non-coding RNAs in yeast reveal context-dependent phenotypes and in trans effects on the protein regulatory network.PLoS Genet. 2021 Jan 25;17(1):e1008761. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008761. eCollection 2021 Jan. PLoS Genet. 2021. PMID: 33493158 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Development in Biomedical Applications of Oligonucleotides with Triplex-Forming Ability.Polymers (Basel). 2023 Feb 9;15(4):858. doi: 10.3390/polym15040858. Polymers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36850142 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Djebali S, Davis CA, Merkel A, Dobin A, Lassmann T, Mortazavi A, Tanzer A, Lagarde J, Lin W, Schlesinger F, et al.. Landscape of transcription in human cells. Nature 2012; 489:101-8; PMID:22955620; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature11233 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rhind N, Chen Z, Yassour M, Thompson DA, Haas BJ, Habib N, Wapinski I, Roy S, Lin MF, Heiman DI, et al.. Comparative functional genomics of the fission yeasts. Science 2011; 332:930-6; PMID:21511999; http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.1203357 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bonasio R, Shiekhattar R. Regulation of transcription by long noncoding RNAs. Annu Rev Genet 2014; 48:433-55; PMID:25251851; http://dx.doi.org/10.1146/annurev-genet-120213-092323 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wei W, Pelechano V, Järvelin AI, Steinmetz LM. Functional consequences of bidirectional promoters. Trends Genet 2011; 27:267-76; PMID:21601935; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.tig.2011.04.002 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Li W, Notani D, Rosenfeld MG. Enhancers as non-coding RNA transcription units: recent insights and future perspectives. Nat Rev Genet 2016; 17:207-23; PMID:26948815; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nrg.2016.4 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
