Number of People Blind or Visually Impaired by Glaucoma Worldwide and in World Regions 1990 - 2010: A Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 27764086
- PMCID: PMC5072735
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0162229
Number of People Blind or Visually Impaired by Glaucoma Worldwide and in World Regions 1990 - 2010: A Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Objective: To assess the number of individuals visually impaired or blind due to glaucoma and to examine regional differences and temporal changes in this parameter for the period from 1990 to 2012.
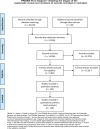
Methods: As part of the Global Burden of Diseases (GBD) Study 2010, we performed a systematic literature review for the period from 1980 to 2012. We primarily identified 14,908 relevant manuscripts, out of which 243 high-quality, population-based studies remained after review by an expert panel that involved application of selection criteria that dwelt on population representativeness and clarity of visual acuity methods used. Sixty-six specified the proportion attributable to glaucoma. The software tool DisMod-MR (Disease Modeling-Metaregression) of the GBD was used to calculate fraction of vision impairment due to glaucoma.
Results: In 2010, 2.1 million (95% Uncertainty Interval (UI):1.9,2.6) people were blind, and 4.2 (95% UI:3.7,5.8) million were visually impaired due to glaucoma. Glaucoma caused worldwide 6.6% (95% UI:5.9,7.9) of all blindness in 2010 and 2.2% (95% UI:2.0,2.8) of all moderate and severe visual impairment (MSVI). These figures were lower in regions with younger populations (<5% in South Asia) than in high-income regions with relatively old populations (>10%). From 1990 to 2010, the number of blind or visually impaired due to glaucoma increased by 0.8 million (95%UI:0.7, 1.1) or 62% and by 2.3 million (95%UI:2.1,3.5) or 83%, respectively. Percentage of global blindness caused by glaucoma increased between 1990 and 2010 from 4.4% (4.0,5.1) to 6.6%. Age-standardized prevalence of glaucoma related blindness and MSVI did not differ markedly between world regions nor between women.
Significance: By 2010, one out of 15 blind people was blind due to glaucoma, and one of 45 visually impaired people was visually impaired, highlighting the increasing global burden of glaucoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Shiose Y, Kitazawa Y, Tsukahara S, Akamatsu T, Mizokami K, Futa R, et al. Epidemiology of glaucoma in Japan—a nationwide glaucoma survey. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 1991;35: 133–155. - PubMed
-
- Tielsch JM, Katz J, Singh K, Quigley HA, Gottsch JD, Javitt J, et al. A population-based evaluation of glaucoma screening: the Baltimore Eye Survey. Am J Epidemiol. 1991;134: 1102–1110. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials