The Spatial Dynamics of Predators and the Benefits and Costs of Sharing Information
- PMID: 27764098
- PMCID: PMC5072596
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1005147
The Spatial Dynamics of Predators and the Benefits and Costs of Sharing Information
Abstract
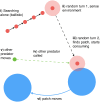
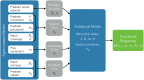
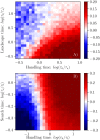
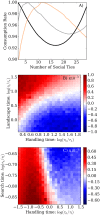
Predators of all kinds, be they lions hunting in the Serengeti or fishermen searching for their catch, display various collective strategies. A common strategy is to share information about the location of prey. However, depending on the spatial characteristics and mobility of predators and prey, information sharing can either improve or hinder individual success. Here, our goal is to investigate the interacting effects of space and information sharing on predation efficiency, represented by the expected rate at which prey are found and consumed. We derive a feeding functional response that accounts for both spatio-temporal heterogeneity and communication, and validate this mathematical analysis with a computational agent-based model. This agent-based model has an explicit yet minimal representation of space, as well as information sharing about the location of prey. The analytical model simplifies predator behavior into a few discrete states and one essential trade-off, between the individual benefit of acquiring information and the cost of creating spatial and temporal correlation between predators. Despite the absence of an explicit spatial dimension in these equations, they quantitatively predict the predator consumption rates measured in the agent-based simulations across the explored parameter space. Together, the mathematical analysis and agent-based simulations identify the conditions for when there is a benefit to sharing information, and also when there is a cost.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Couzin ID, Krause J Self-organization and collective behavior in vertebrates. Advances in the Study of Behavior. 2003;32:1–75. 10.1016/S0065-3454(03)01001-5 - DOI
-
- Bastardie F, Nielsen JR, Andersen BS, Eigaard OR. Effects of fishing effort allocation scenarios on energy efficiency and profitability: An individual-based model applied to Danish fisheries. Fisheries Research. 2010;106(3):501–516. 10.1016/j.fishres.2010.09.025 - DOI
-
- Evans KS, Weninger Q Information sharing and cooperative search in fisheries. Environmental and Resource Economics. 2014;58(3):353–372. 10.1007/s10640-013-9701-8 - DOI
-
- Gatewood JB. Cooperation, Competition, and Synergy: Information-sharing Groups among Southeast Alaskan Salmon Seiners. American Ethnologist. 1984;11(2):350–370. 10.1525/ae.1984.11.2.02a00080 - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

