Immunomodulatory Effects of Different Lactic Acid Bacteria on Allergic Response and Its Relationship with In Vitro Properties
- PMID: 27764153
- PMCID: PMC5072832
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0164697
Immunomodulatory Effects of Different Lactic Acid Bacteria on Allergic Response and Its Relationship with In Vitro Properties
Abstract
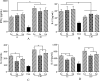
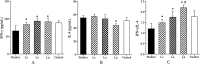
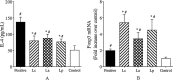
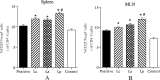
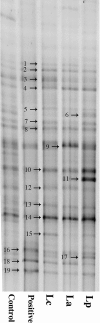
Some studies reported that probiotic could relieve allergy-induced damage to the host, but how to get a useful probiotic is still a challenge. In this study, the protective effects of three lactic acid bacteria (La, Lp and Lc) were evaluated in a mouse model, and its relationship with the in vitro properties was analyzed. The in vitro results indicated that La with the capacity to inhibit IL-4 production could have a better anti-allergy effect in vivo than two others. However, the animal trials showed that all LAB strains could alleviate allergen-induced airway inflammation. Among them, LAB strain Lp had a better effect in inhibiting allergic response through a modulation of Th1/Th2 balance and an increase of regulatory T cells. This difference could be explained by that different LAB strains have a strain-specific effect on gut microbiota closely associated with host immune responses. Finally, this study did not only obtain an effective anti-allergy probiotic strain via animal study, but also indicate that probiotic-induced effect on intestinal microbiota should be considered as an important screening index, apart from its inherent characteristics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
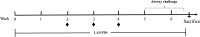


References
-
- Matasar MJ, Neugut AI. Epidemiology of anaphylaxis in the United States. Current allergy and asthma reports. 2003;3(1):30–35. - PubMed
-
- Salminen S, Von Wright A. Lactic acid bacteria: microbiological and functional aspects: CRC Press; 2004.
-
- Schaafsma G. State of the art concerning probiotic strains in milk products NEWSLETTER-INTERNATIONAL DAIRY FEDERATION; 1996:23–23.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

