In Situ Transcription Profiling of Single Cells Reveals Spatial Organization of Cells in the Mouse Hippocampus
- PMID: 27764670
- PMCID: PMC5087994
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2016.10.001
In Situ Transcription Profiling of Single Cells Reveals Spatial Organization of Cells in the Mouse Hippocampus
Abstract
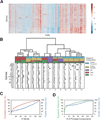
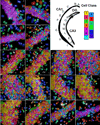
Identifying the spatial organization of tissues at cellular resolution from single-cell gene expression profiles is essential to understanding biological systems. Using an in situ 3D multiplexed imaging method, seqFISH, we identify unique transcriptional states by quantifying and clustering up to 249 genes in 16,958 cells to examine whether the hippocampus is organized into transcriptionally distinct subregions. We identified distinct layers in the dentate gyrus corresponding to the granule cell layer and the subgranular zone and, contrary to previous reports, discovered that distinct subregions within the CA1 and CA3 are composed of unique combinations of cells in different transcriptional states. In addition, we found that the dorsal CA1 is relatively homogeneous at the single cell level, while ventral CA1 is highly heterogeneous. These structures and patterns are observed using different mice and different sets of genes. Together, these results demonstrate the power of seqFISH in transcriptional profiling of complex tissues.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures






Comment in
-
Editorial Note to: In Situ Transcription Profiling of Single Cells Reveals Spatial Organization of Cells in the Mouse Hippocampus.Neuron. 2017 May 17;94(4):745-746. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2017.05.009. Neuron. 2017. PMID: 28521128 No abstract available.
References
-
- Betzig E, Patterson GH, Sougrat R, Lindwasser OW, Olenych S, Bonifacino JS, Davidson MW, Lippincott-Schwartz J, Hess HF. Imaging Intracellular Fluorescent Proteins at Nanometer Resolution. Science. 2006;313:1642–1645. - PubMed
-
- Breiman L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001;45:5–32.
-
- Cembrowski MS, Bachman JL, Wang L, Sugino K, Shields BC, Spruston N. Spatial Gene-Expression Gradients Underlie Prominent Heterogeneity of CA1 Pyramidal Neurons. Neuron. 2016;89:351–368. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

