Incorporating Risk Factors to Identify the Indication of Post-mastectomy Radiotherapy in N1 Breast Cancer Treated with Optimal Systemic Therapy: A Multicenter Analysis in Korea (KROG 14-23)
- PMID: 27764904
- PMCID: PMC5512365
- DOI: 10.4143/crt.2016.405
Incorporating Risk Factors to Identify the Indication of Post-mastectomy Radiotherapy in N1 Breast Cancer Treated with Optimal Systemic Therapy: A Multicenter Analysis in Korea (KROG 14-23)
Abstract
Purpose: In a recent meta-analysis, post-mastectomy radiotherapy (PMRT) reduced any first recurrence (AFR) and improved survival in N1 and N2 patients. We investigated risk factors for AFR in N1 after optimal systemic therapy without PMRT, to define a subgroup of patients who may benefit from PMRT.
Materials and methods: One thousand three hundred eighty-two pT1-2N1M0 breast cancer patients treated with mastectomy without PMRT between 2005 and 2010 were retrospectively analyzed. Only 0.6% had no systemic therapy.
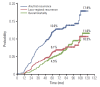
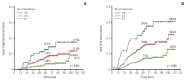
Results: After a median follow-up of 5.9 years, there were 173 AFR (53 loco-regional recurrence [LRR] without distant metastases [DM], 38 LRR with DM, and 82 DM without LRR). The 5-year LRR and AFR rates were 6.1% and 12.0%, respectively. Multivariate analysis revealed that close resection margin (p=0.001) was the only independent risk factor for LRR. Multivariate analysis for AFR revealed that age < 35 years (p=0.025), T2 stage (p=0.004), high tumor grade (p=0.032), close resection margin (p=0.035), and triple-negative biological subtype (p=0.031) were independent risk factors. Two or three positive lymph nodes (p=0.078) were considered a marginally significant factor. When stratified by these six factors, the 5-year LRR rates were 3.6% with 0-1 (n=606), 7.5% with 2-3 (n=655), and 12.7% with 4-6 (n=93) risk factors. The 5-year AFR rates were 7.1% with 0-1, 15.0% with 2-3, and 24.5% with 4-6 risk factors.
Conclusion: Patients with pT1-2N1M0 breast cancer who underwent mastectomy and optimal systemic therapy showed excellent loco-regional control and disease control. The patients with four or more risk factors may benefit from PMRT, and those with two or three risk factors merit consideration of PMRT.
Keywords: Breast neoplasms; Post-mastectomy radiotherapy; Risk factors.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest relevant to this article was not reported.
Figures
References
-
- Gradishar WJ, Anderson BO, Balassanian R, Blair SL, Burstein HJ, Cyr A, et al. Invasive Breast Cancer Version 1.2016, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2016;14:324–54. - PubMed
-
- Recht A, Edge SB, Solin LJ, Robinson DS, Estabrook A, Fine RE, et al. Postmastectomy radiotherapy: clinical practice guidelines of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. J Clin Oncol. 2001;19:1539–69. - PubMed
-
- EBCTCG (Early Breast Cancer Trialists' Collaborative Group) McGale P, Taylor C, Correa C, Cutter D, Duane F, et al. Effect of radiotherapy after mastectomy and axillary surgery on 10-year recurrence and 20-year breast cancer mortality: meta-analysis of individual patient data for 8135 women in 22 randomised trials. Lancet. 2014;383:2127–35. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical